Figure 1.
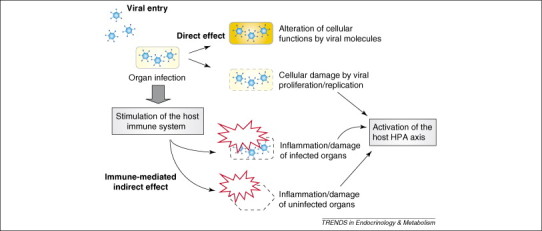
Virus-mediated modification of host endocrine organs. Viruses damage infected cells directly by proliferating inside cells, and can modulate cellular functions through molecules that are encoded by their genetic material. Viral infection might also trigger an inflammatory response, with consequent damage of both infected and uninfected tissues. Virus-induced tissue inflammation might increase the production of systemic mediators of inflammation, which, in turn, might stimulate the host HPA axis/stress system.
