Fig. 4.
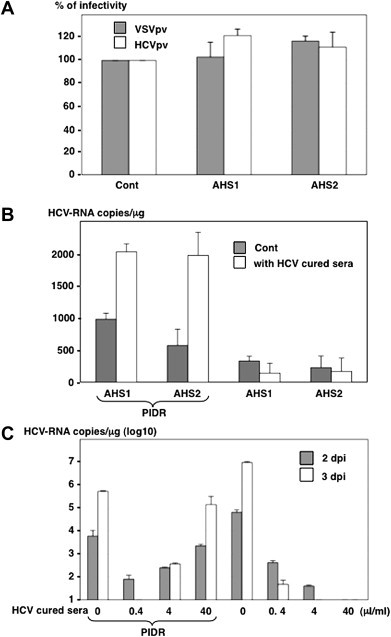
Neutralizing antibodies in the CHS enhanced the PIDR-mediated entry of HCV. (A) The absence of neutralizing antibodies in the sera from acute hepatitis C patients (AHS) was determined by a neutralization assay using the HCVpv (white bars) and VSVpv (gray bar). (B) The effect of PIDR on the entry of HCVser into Huh7OK1 cells in the presence of neutralizing antibodies. The AHS were incubated with the CHS carrying neutralization antibodies but no infectious HCV obtained from patients cured by the IFN therapy (white bars) or HDS (gray bar) in the presence (left) or absence (right) of PIDR and inoculated into Huh7OK1 cells. The HCV-RNA titers in cells were determined at 24 h post-inoculation. (C). The effect of neutralizing antibodies on the PIDR-mediated infection of HCVcc. Huh7OK1 cells were inoculated with HCVcc at an MOI of 0.05 after incubation with 0.4–40 μl/ml of HCV-negative CHS in the presence (left) or absence (right) of PIDR. Gray and white bars indicate the HCV-RNA titers at 2 and 3 days after infection, respectively.
