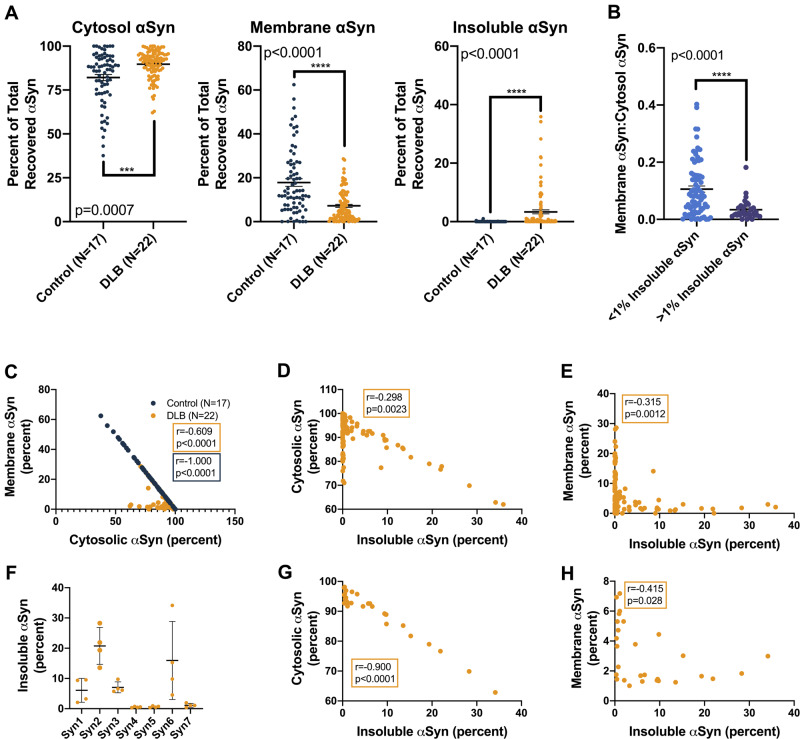
Figure 2.
αSyn solubility distribution in DLB versus control brains based on the percentage of total analysis. (A) For each tissue piece (represented by a single point), the ELISA-measured αSyn concentration was multiplied by the original volume of the extract, yielding the total αSyn in each fraction. This was then expressed as a percentage of the total αSyn recovered in all three fractions. Graphs: percentage of total αSyn in the cytosolic, membrane (1% Triton-soluble) and insoluble (SDS/8 M urea-soluble) extracts. Between three and eight tissue pieces were processed and analysed per brain, and each piece was measured in triplicate. Bars: means with SEMs. Control and DLB extracts were compared using the Mann–Whitney comparison of ranks. (B) DLB brain extracts were stratified based on insoluble αSyn quantities (blue: <1% of total extracted αSyn; purple: >1% of total extracted αSyn), and the ratio of membranous to cytosolic αSyn was calculated for each group. Proportionally, this analysis revealed higher membranous αSyn in low-pathology DLB extracts (P < 0.0001, Mann–Whitney comparison of ranks). (C) Correlation analyses of the percentages of recovered αSyn in the cytosolic and membrane cortical fractions, both from control subject and DLB patient brains, showed strong negative associations, an unsurprising finding given that these fractions contain most of the total extracted αSyn (control: Spearman r = −1.000, 95% CI: −1.000 to −1.000, 2-tailed P < 0.0001; DLB: Spearman r = −0.609, 95% CI: −0.721 to −0.462, P < 0.0001). (D and E) Strong negative associations also exist between the percentage of total extracted αSyn in the insoluble fraction and the percentage of total extracted αSyn in both the cytosolic and membrane-associated fractions across all cortical extracts from DLB patient brains (insoluble versus cytosol: Spearman r = −0.298, 95% CI: −0.469 to −0.105, P = 0.0023; insoluble versus membrane: Spearman r = −0.315, 95% CI: −0.484 to −0.124, P = 0.0012). (F) In terms of insoluble αSyn as a percentage of total extracted αSyn, DLB patient brains from the Mayo Clinic brain bank showed the highest pathological burden. Means with standard deviations are shown. (G and H) Correlation analyses comparing the percentage of total extracted αSyn in insoluble fractions to cytosolic and membrane-associated fractions from these high-burden Mayo Clinic brains showed even stronger negative associations than the analyses that included DLB patient brains from all sources (insoluble versus cytosol: Spearman r = −0.900, 95% CI: −0.954 to −0.89, P < 0.0001; insoluble versus membrane: Spearman r = −0.415, 95% CI: −0.689 to −0.386, P = 0.0028).