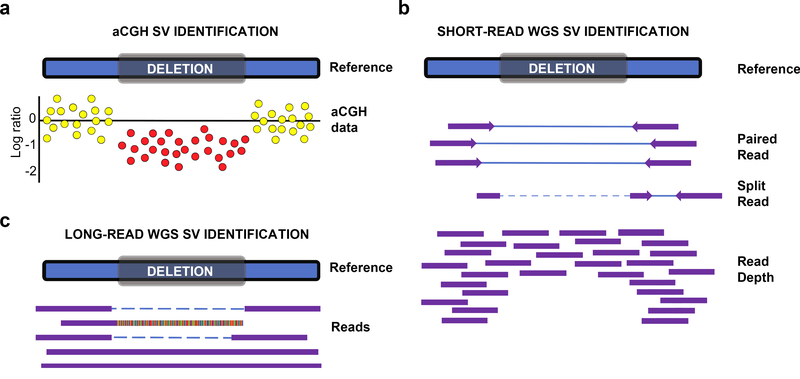
Fig. 2. Heterozygous deletion detection.
A depiction of deletion detection by aCGH, short-read and long-read whole genome sequencing (WGS) technologies. a. In aCGH, colored dots represent the signal ratio between the reference and sample for hybridization to a probe at that locus. Normal signals are represented with yellow dots and loss in signal is represented with red. On a log scale, copy neutral regions are indicated as 0, heterozygous deletions are −1 and homozygous deletions are −2. b. Using short-read WGS data, deletion signatures are identified using paired-end reads (read spans the deletion), split-reads (read containing the deletion; breakpoint precision), and read-depth (number of reads around the deletion locus; better suited at differentiating zygosity) information. c. In long-read WGS data, reads can span the entire deletion or can extend into the deletion and therefore represent split reads events.