Figure 5.
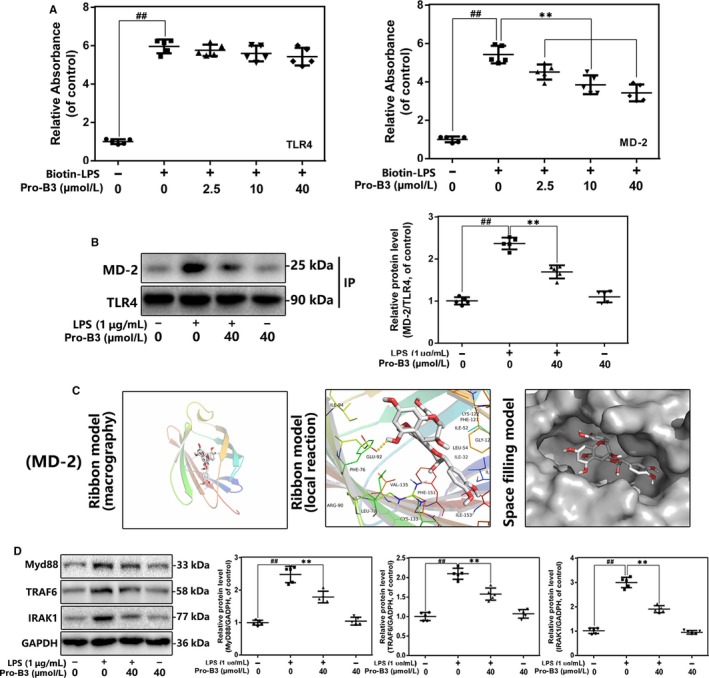
Influence of Pro‐B3 on LPS‐induced TLR4/MD‐2 signalling activation. A, The binding of biotin‐labelled LPS to rhMD‐2 and rhTLR4 was examined by competitive ELISA. B,The complexes of TLR4‐MD‐2 in NP cells treated as above were detected by immunoprecipitation. C, Pro‐B3 was docked with the MD‐2 structure. Docking studies were performed as described in Materials and methods. The protein residues are shown in a ribbon model. The proposed binding pose of Pro‐B3 shows interactions with GLU‐92. The space filling models show the binding of Pro‐B3 in the inhibitory binding pockets. D, The protein expressions of MyD88, IRAK‐1 and TRAF‐6 in NP cells treated as above were detected by Western blot. The data in the figures represent the averages ± SD Significant differences among different groups are indicated as ## P < .01, vs control group; **P < .01 vs LPS alone treatment group, n = 5
