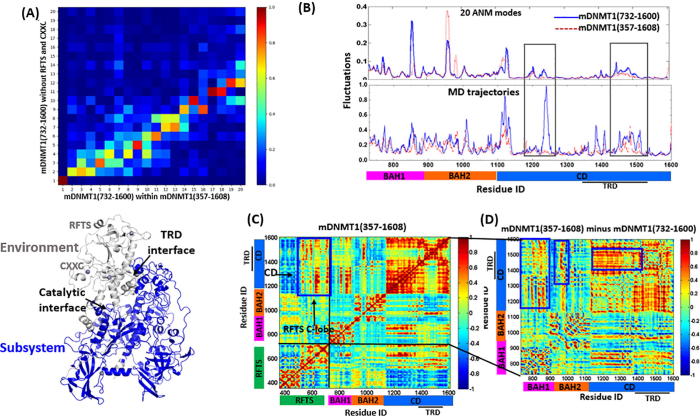
Fig. 4.
Difference of intrinsic dynamics between mDNMT1 (357–1608) and mDNMT1 (732–1600). (A) The overlap values represented by the correlations between the top 20 modes accessible to mDNMT1 (732–1600) alone and in the whole mDNMT1 (357–1608) (upper panel). The mDNMT1 (732–1600) stands for the subsystem represented in blue and the RFTS and CXX C region stand for the environment in gray (lower panel). (B) The square fluctuations of 20 ANM modes in mDNMT1 (732–1600) and mDNMT1 (357–1608) (Upper panel). The square fluctuations for the trajectories of MD simulations in mDNMT1 (732–1600) and hDNMT1 (351–1600) (Lower panel). (C) The cross-correlation map of the 100 slowest modes for mDNMT1 (357–1608). (D) The difference map of cross-correlations between mDNMT1 (732–1600) and mDNMT1 (357–1608). In particular, the larger positive correlations between BAH1 and CD, between BAH2-TRD loop and CD, as well as between the TRD region and the residues in CD core have been highlighted (blue boxes). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)