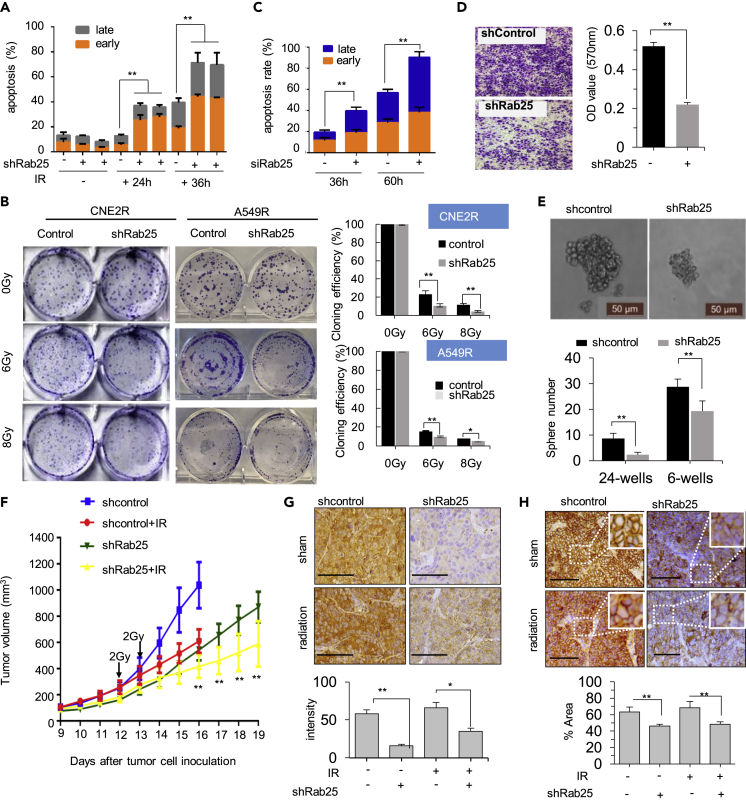
Figure 6.
Blocking Rab25 Enhances Cell Death and Radio-Sensitization In Vitro and In Vivo
(A) Apoptosis rate in CNE2R or CNE2R cells transfected with shRab25 24 or 36 h after 4 Gy radiation.
(B) Clonogenic survival of radiation in radioresistant cells with shRab25-mediated knockdown. The clonogenicity was calculated by normalizing to the control cells that received 0 Gy IR, and the normalized clonogenic survival rates are shown on the bottom (n = 3, mean ± SD, ∗p < 0. 05, ∗∗p < 0. 01).
(C) Apoptosis rate after cells cultured in ultra-low attached wells for indicated time.
(D) Images and capacity of trans-well invasion (au, arbitrary units; n = 3; mean ± SD, ∗∗p < 0.01).
(E) Mammosphere formation assay (n = 3 in each group, mean ± SD, ∗∗p < 0.01), scale bar, 50 μm.
(F) Radiosensitivity of xenograft tumors generated with control and CNE2R-shRab25 cells and treated with 2 Gy at day 12 and day 13 (n = 5; mean ± SD, ∗∗p < 0.01).
(G) Representative images of IHC staining for Rab25 in NPC xenografts with or without irradiation. The average Rab25-positive cells in tumors were quantified and shown in the right bar graph. Scale bar, 50 μm. Mean ± SD, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.
(H) Representative images of IHC staining for EGFR in NPC xenografts with or without irradiation. The average EGFR-positive cells in tumors were quantified and shown in the right bar graph. Scale bar, 50 μm. mean ± SD, ∗∗p < 0.01.