Figure EV2. RNAi of ECT2/Pbl leads to enlarged cells (cytokinesis defect) or extrusion of cells from the epithelium and subsequent apoptosis (spindle orientation defect) in the Drosophila wing disc.
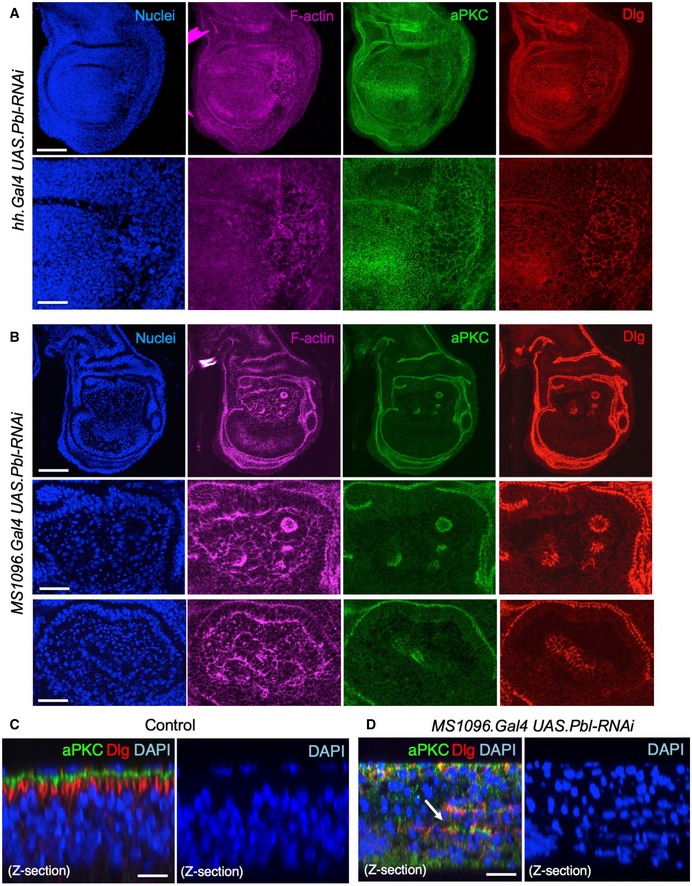
- Third instar wing imaginal disc expressing UAS.Pbl‐RNAi in the posterior compartment driven by the hh.Gal4 line. Note enlarged cells (marked by F‐actin, aPKC or Dlg staining). DAPI marks nuclei. Scale bars ˜20 μm (low mag) ˜5 μm (high mag). n > 6 independent biological replicates.
- Third instar wing imaginal disc expressing UAS.Pbl‐RNAi in the entire wing pouch driven by the MS1096.Gal4 line. Note many extruded cells (marked by F‐actin, aPKC or Dlg staining). DAPI marks nuclei, including many pyknotic nuclei due to apoptosis. Scale bars ˜20 μm (low mag) ˜5 μm (high mag). n > 7 independent biological replicates.
- Control cross‐section of wild‐type third instar wing disc stained for aPKC, Dlg and nuclei (DAPI). Scale bar ˜2 μm. n > 4 independent biological replicates.
- Cross‐section of third instar wing imaginal disc expressing UAS.Pbl‐RNAi in the entire wing pouch driven by the MS1096.Gal4 line. Note extrusion of cells (revealed by staining for aPKC, Dlg) and many pyknotic nuclei (DAPI staining). Arrow shows residual polarised apical domains in cells that have been extruded. Scale bar ˜2 μm. n > 9 independent biological replicates.
