Figure EV5. Overexpression of ECT2/Pbl leads to Cdc42‐dependent ectopic spreading of aPKC and cell rounding in the Drosophila follicle cell epithelium.
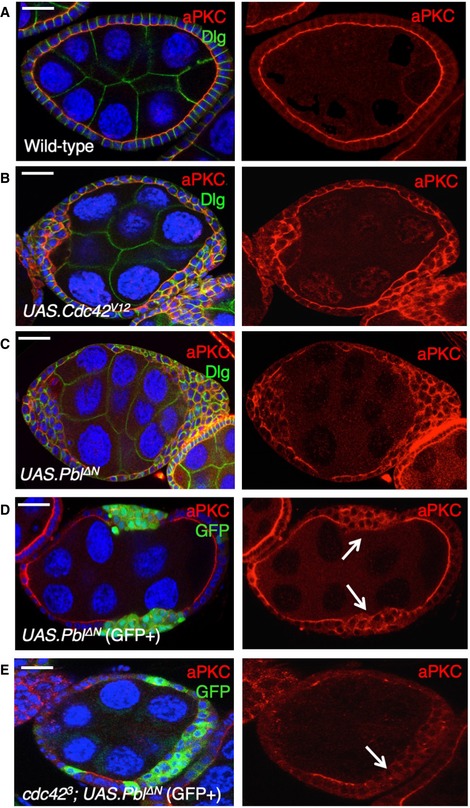
- Wild‐type stage 7 egg chamber showing normal localisation of aPKC and Dlg in the follicle cell epithelium. Scale bar ˜6 μm. n > 4 independent biological replicates.
- tj.Gal4‐driven UAS.Cdc42 V12 causes ectopic spreading of aPKC in most cells. Scale bar ˜6 μm. n > 3 independent biological replicates.
- tj.Gal4‐driven UAS.Pbl‐deltaN causes ectopic spreading of aPKC in most cells. Scale bar ˜6 μm. n > 6 independent biological replicates.
- MARCM clonal induction of UAS.Pbl‐deltaN and UAS.GFP causes ectopic spreading of aPKC in most GFP‐positive cells. Scale bar ˜6 μm. n > 5 independent biological replicates. Arrows point to GFP+ clones.
- MARCM induction of UAS.Pbl‐deltaN and UAS.GFP in cdc42 3 mutant clones causes loss of aPKC in most GFP‐positive cells. This result indicates that overexpressed Pbl acts upstream of Cdc42 to control aPKC localisation. Scale bar ˜6 μm. n > 3 independent biological replicates. Arrows point to GFP+ clones.
