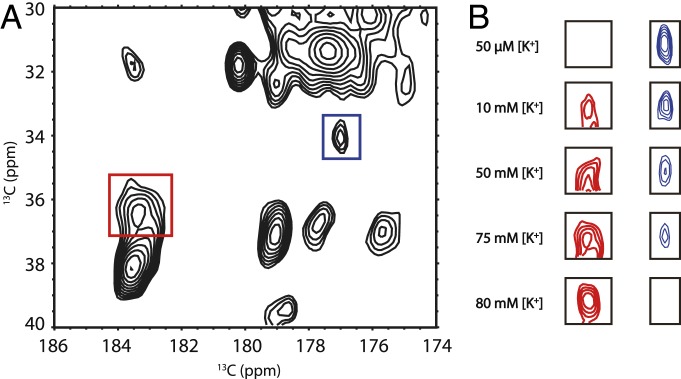
Fig. 3.
The effect of [K+] on the E120 residue in the pH gate of the H25R/E118A KcsA mutant at pH 7.5. (A) The 2D 13C-13C correlation spectrum of open pH gate KcsA at 75 mM [K+]. The peaks in the red and blue rectangles are the E120 CG−CD peaks in deprotonated and protonated state, respectively. (B) The protonated and deprotonated state change of the E120 peak across various [K+]. Protonated and deprotonated E120 CG−CD peaks at 50 μM and 10, 50, 75, and 80 mM are shown. At pH 7.5, E120 is protonated at low [K+]; while, at 80 mM [K+] and above, E120 is completely deprotonated. In samples with [K+] larger than 80 mM, the E120 CG−CD peaks are all in the deprotonated state. This protonation state change provides clear evidence for pKa change of the glutamic acid residue.