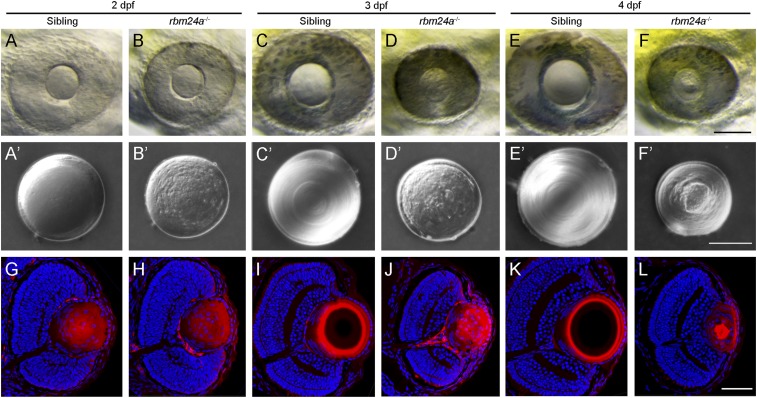
Fig. 2.
Cataract phenotype and lens differentiation defects in rbm24a mutants. (A–F) Live images compare eye phenotypes between WT siblings and time-matched rbm24a mutants from 2 to 4 dpf. (Scale bar, 100 µm.) (A′–F′) Differential interference contrast images illustrate the cataract phenotype in surgically dissected lenses. In WT siblings, the lens progressively increases in size, with fiber cells forming regular and refractive concentric layers. In rbm24a mutants, the lens shows no growth, with an irregular surface and a granular aspect. (Scale bar, 50 µm.) (G–L) Staining of lens sections with phalloidin and Hoechst 33342 at the level of the optic nerve compares fiber cell organization and denucleation between WT siblings and rbm24a mutants. (Scale bar, 50 µm.)