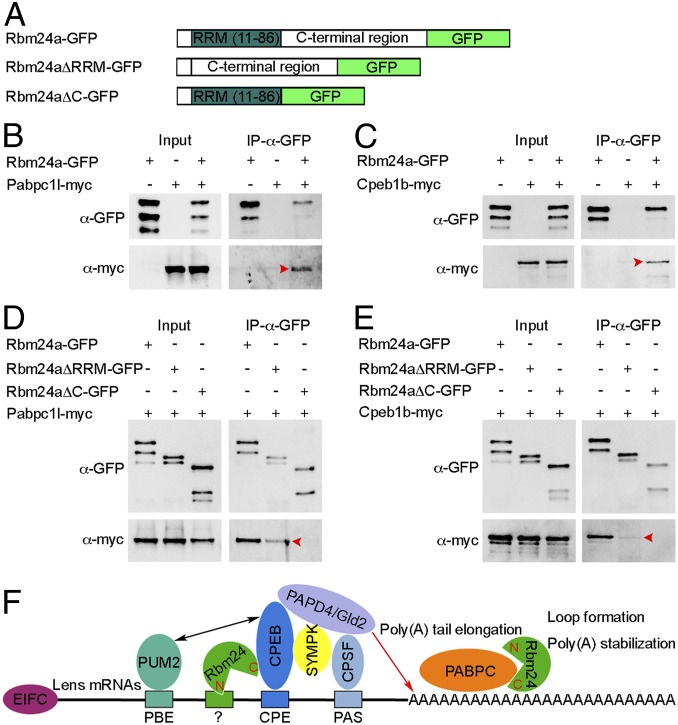
Fig. 8.
Rbm24a physically interacts with Pabpc1l and Cpeb1b through the C-terminal region. (A) Schematic representation of GFP-tagged full-length and truncated Rbm24a proteins. (B and C) The full-length Rbm24a interacts with Pabpc1l and Cpeb1b (arrowheads). (D and E) The C-terminal region of Rbm24a coimmunoprecipitates with Pabpc1l and Cpeb1b (arrowheads), but the interaction with Cpeb1b is weak. (F) Possible function of vertebrate Rbm24 in poly(A) tail elongation and stabilization. In the lens, Rbm24 directly associates with CPEB and promotes the activity of PAPD4/Gld2 poly(A) polymerase in poly(A) tail elongation; it also interacts with PABPC to facilitate loop formation and stabilize poly(A) tail. The RNA motif that recruits Rbm24 remains to be determined. EIFC, eukaryotic translation initiation factor complex; PBE, PUM2-binding element; CPE, cytoplasmic polyadenylation element; PAS, polyadenylation signal; N, Rbm24 N-terminal region; C, Rbm24 C-terminal region.