Fig. 3.
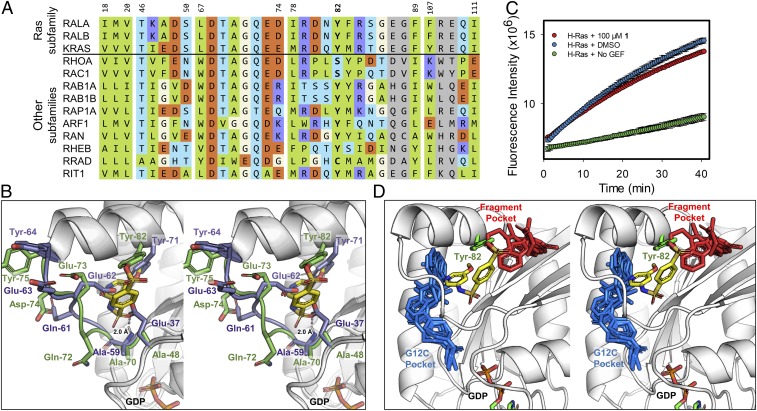
Compound 1 selectively inhibits Ral over Ras. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of representative members of the Ras superfamily to RalA. Residues are colored according to the scheme in Fig. 2H. Residue numbers are in reference to their respective position on RalA. Multiple sequence alignment was performed using Clustal Omega (v1.2.4) (61). (B) Stereo image of RalA–1 complex (green loops and carbons) superimposed with K-Ras (PDB ID code: 4EPV; purple loops and carbons). RalA residues are labeled in green and K-Ras residues are labeled in purple. (C) Inhibition of SOS-mediated guanine nucleotide exchange of K-Ras by 100 µM 1 after 24-h incubation at 4 °C (mean ± SD, n = 2). (D) Small molecule compounds bound to K-Ras are superimposed onto the binding mode of RalA-1. RalA is shown in white cartoon with the covalently bound RalA-Tyr82 and 1 compound shown as green and yellow sticks, respectively. Compounds that target the G12C mutation of K-Ras (blue sticks; PDB ID codes: 4M22, 5V6S, 5V9U, 5YXZ, 6N2J) and noncovalent fragments of K-Ras (red sticks; PDB ID codes: 4DSO, 4EPT, 4EPV, 4EPW, 4PZY) target adjacent binding pockets on K-Ras.