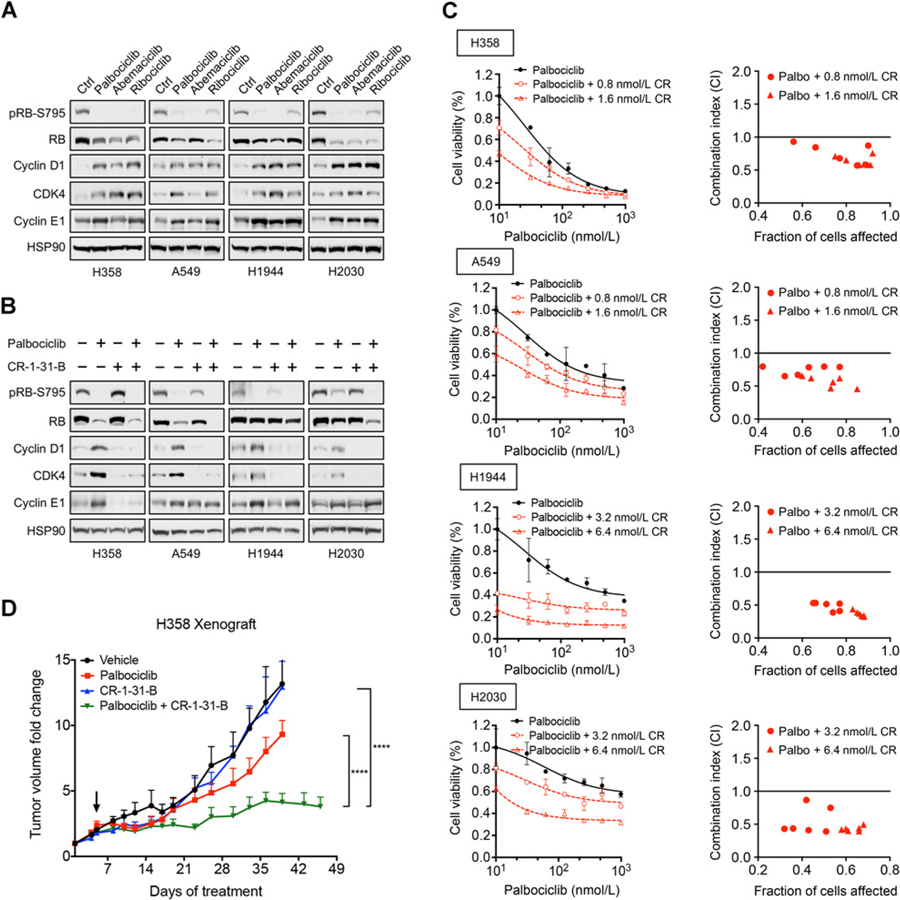
Figure 4.
Combination treatment targeting eIF4A and CDK4/6 synergistically suppresses proliferation of KRAS-mutant NSCLC cells. A, Immunoblot analysis showing upregulation of cyclin D1, CDK4, and cyclin E1 of four KRAS-mutant NSCLC cell lines (H358, A549, H1944, and H2030) treated with CDK4/6 inhibitors. Cells were treated for 24 hours with 300 nmol/L palbociclib, 150 nmol/L abemaciclib, or 1 μmol/L ribociclib. B, Immunoblot showing treatment of CR-1–31-B suppresses upregulation of cyclin D1, CDK4, and cyclin E1 induced by palbociclib in KRAS-mutant NSCLC cells. Cells were treated for 48 hours with 300 nmol/L palbociclib, 3.2 nmol/L CR-1–31-B, or their combination. C, Cell viability assays and isobologram synergy analysis of four KRAS-mutant NSCLCs treated with multiple combination doses of CR-1–31-B and palbociclib. Cells were treated with increasing concentrations of palbociclib and/or CR-1–31-B for 5 to 8 days, and cell viability was measured using CellTiter-Blue. Error bars represent mean ± SD. Combination indices were calculated for multiple doses of palbociclib and CR-1–31-B for all four NSCLC cell lines. D, Tumor growth curves of H358 subcutaneous xenografts in NSG mice treated with vehicle (n = 5), palbociclib (45 mg/kg; n = 4), CR-1–31-B (0.2 mg/kg; n = 4), or palbociclib + CR-1–31-B combination (n = 4). Mice treated daily starting on day 5 (arrow) for 1 week and recovered for 1 week. Following recovery, mice were treated daily until endpoint. Error bars indicate SEM values. ****, P < 0.0001; by two-way ANOVA.