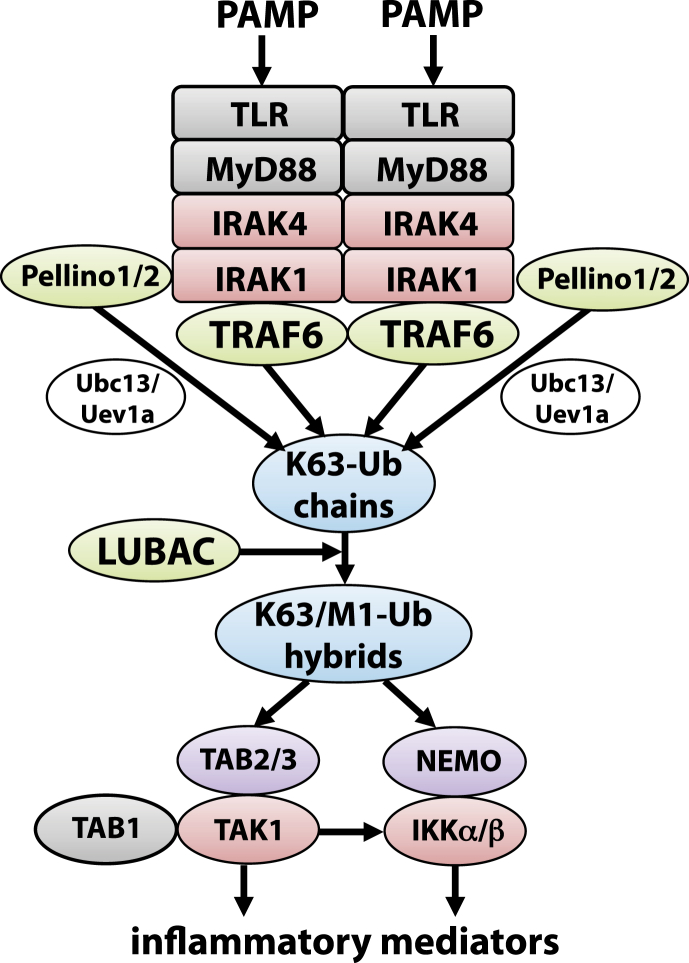
Fig. 2.
TLR signalling triggers the formation of Lys63/Met1-linked hybrid ubiquitin chains and activation of the TAK1 and IKK complexes. The interaction of PAMPs with TLRs triggers the formation of an oligomeric complex termed the Myddosome, comprising the adaptor protein MyD88 and protein kinases of the IRAK family. IRAKs 1 and 2 induce the activation of the E3 ligase TRAF6 while IRAK1 also phosphorylates and activates the E3 ligases Pellino 1 and 2. The three E3 ligases form productive complexes with the E2 conjugating complex Ubc13-Uev1a leading to the formation of Lys63-linked ubiquitin chains, which bind to the TAB2 and TAB3 subunits of the TAB1-TAK1-TAB2 and TAB1-TAK1-TAB3 complexes activating these protein kinases. The Lys63-linked ubiquitin chains also become a substrate for the HOIP-component of LUBAC, which is recruited into the signalling complex, forming Lys63/Met1-linked ubiquitin hybrids that recruit the canonical IKK complex. The interaction of Met1-Ub chains with the NEMO component of the IKK complex induces a conformational change that allows TAK1 to initiate the activation of the IKK complex by phosphorylating Ser176/177 of IKKα/β, the activation being completed by the IKKα/β-catalysed autophosphorylation of Ser180/181. Protein kinases are highlighted in red, E3 ligases in green, ubiquitin-binding proteins in purple and ubiquitin chains in blue.