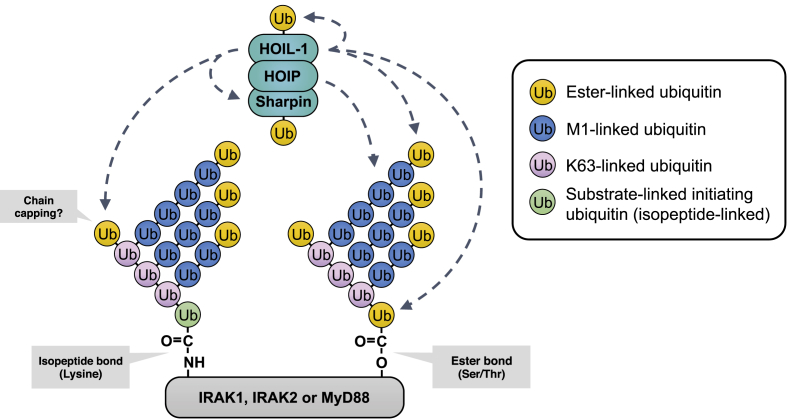
Fig. 5.
Schematic of the linkage types present within the ubiquitin chains attached to components of the Myddosome. Two types of Ub chain are attached to IRAK1, IRAK2 and MyD88. One is initiated by the attachment of ubiquitin to a serine or threonine residue(s) on these proteins and is catalysed by HOIL-1, while the other is initiated by the formation of an isopeptide bond to a lysine residue(s). Ubiquitin is also attached covalently to HOIL-1 and Sharpin by ester bonds. HOIL-1 can additionally catalyse the formation of ubiquitin dimers linked by an oxyester bond in vitro, but whether these linkages are present in the ubiquitin chains that become attached to IRAK1, IRAK2 and MyD88 during TLR signalling is not established. In the schematic we speculatively place such linkages at the terminal K63-Ub and M1-Ub linkages as a “capping” mechanism to explain why the ubiquitin chains that become attached to IRAK1 and IRAK2 are much larger in macrophages from mice expressing an E3 ligase-inactive mutant of HOIL-1 (Fig. 4C and D).