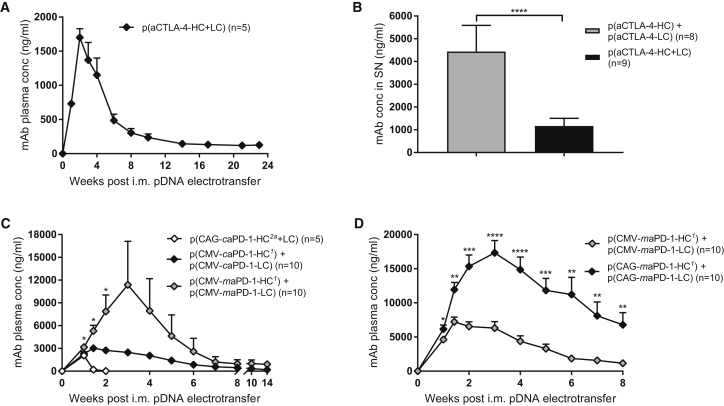
Figure 1.
Engineering of a DNA-Based Anti-CTLA-4 mAb and DNA-Based Anti-PD-1 mAb
mAb concentrations were determined in plasma after a single intramuscular (i.m.) electrotransfer of 60 μg pDNA in C57BL/6J mice (A, C, and D), and in cell supernatant (SN) after transfection of five million 293F Freestyle suspension cells with 5 μg pDNA (B). (A) Validation of anti-CTLA-4 mAb expression by p(aCTLA-4-HC+LC) (n = 5 mice). (B) Comparison of p(aCTLA-4-HC) + p(aCTLA-4-LC) and an equimolar amount of p(aCTLA-4-HC+LC). Data were analyzed with an unpaired t test (n = 8 or 9 biological replicates). (C) Comparison of p(CAG-caPD-1-HC2a+LC), p(CMV-caPD-1-HC1) + p(CMV-caPD-1-LC), and p(CMV-maPD-1-HC1) + p(CMV-maPD-1-LC). Asterisks indicate the statistical difference between the p(CMV-caPD-1) and p(CMV-maPD-1) group, analyzed with an unpaired t test (n = 5 or 10 mice per group). (D) Comparison of the CMV-based and CAG-based pDNA constructs to express the murinized IgG1 anti-PD-1 mAb. mAb plasma concentrations were compared with an unpaired t test (n = 10 mice per group). All data are represented as mean + SEM (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001).