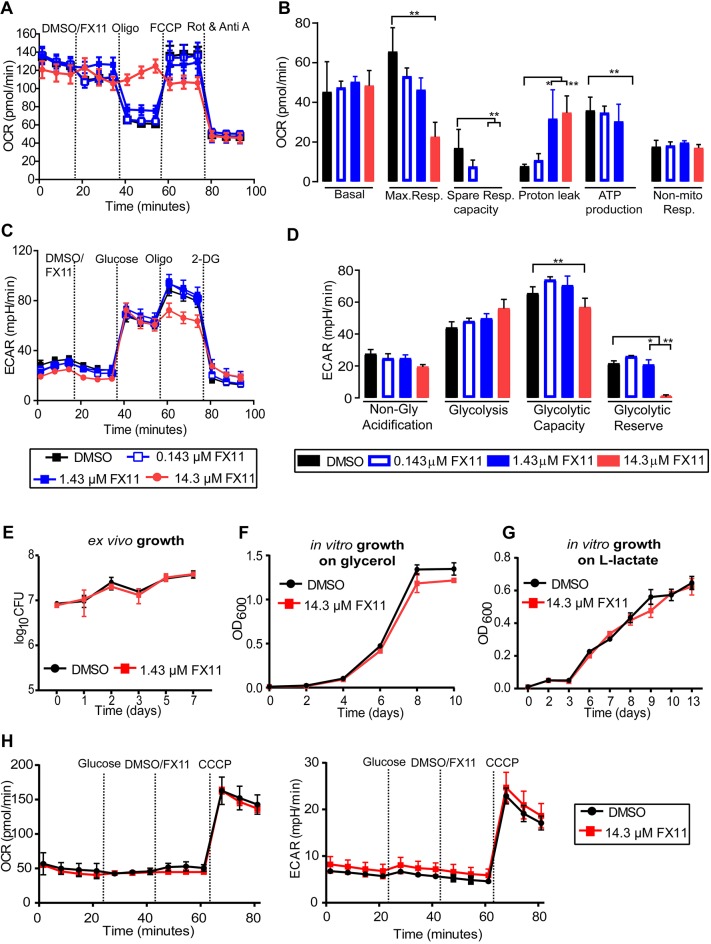
Fig. 1.
FX11-induced metabolic changes are highly host specific. (A-D) FX11 alters the respiratory profile and parameters (A,B), and glycolytic parameters (C,D) of IFN-γ-stimulated murine bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) in a concentration-dependent manner. Wells with DMSO served as a control. Different mitochondrial and glycolytic modulators were sequentially injected and cellular responses (OCR and ECAR values) were measured using a Seahorse XF analyzer. The error bars are standard deviations of the data from three independent experiments. Statistical significance was determined by Student's t-test for each of the concentrations, compared to the DMSO control. Adjusted P-values were corrected for multiple testing using the Benjamini-Hochberg correction, as indicated. *P<0.001, **P<0.0001. In addition, linear regression analysis was carried out to independently determine the statistical significance (see Supplementary Materials and Methods). (E) IFN-γ-stimulated BMDMs infected with M. tuberculosis H37Rv at a multiplicity of infection of 1:5, with FX11 effect determined by enumerating viable bacterial counts. (F,G) Effect of FX11 on M. tuberculosis growth in liquid medium containing 0.2% v/v glycerol (F) or 10 mM sodium L-lactate (G) as the sole carbon source. (H) Effect of FX11 on M. tuberculosis respiratory function [OCR (left) and ECAR (right) values] measured by Seahorse XFp extracellular flux analyzer. DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; ECAR, extracellular acidification rate; FCCP, carbonyl cyanide-4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone; OCR, oxygen consumption rate; OD600, optical density at a wavelength of 600 nm; Rot & Anti A, Rotenone and Antimycin A; 2-DG, 2-deoxy-D-glucose.