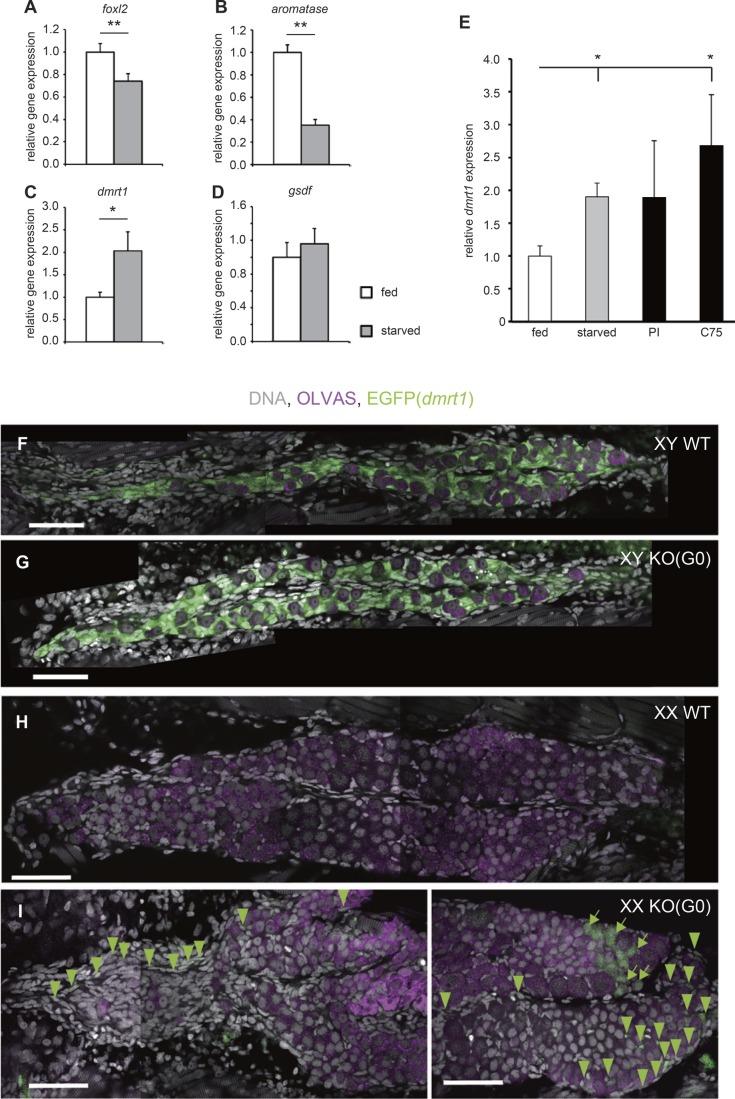
Fig. 4.
dmrt1 is necessary for starvation-induced sex reversal. (A–D) RT-qPCR analysis of foxl2 (A), aromatase (B), dmrt1 (C) and gsdf (D) transcripts extracted from one whole XX larva at 5 dph (fed n=16, starved n=13). Starvation causes the suppression of expression of female related-genes (foxl2 and aromatase) and increase of expression of male related-gene (dmrt1). The values indicate the average and the bars indicate s.e.m. Student's t-test was used as statistical analysis. *P-value<0.05, **P-value<0.01. (E) RT-qPCR analysis of dmrt1 transcripts extracted from one whole XX larva at 5 dph under fed (n=8), starved (n=6), 50 µM Pank inhibitor (n=7), and 20 µg/ml C75 (n=6) treatment conditions. dmrt1 expression is increased by the treatment which induces female-to-male sex reversal. The values indicate the average and the bars indicate s.e.m. P-values from Student's t-test were corrected by Bonferroni correction. *P-value<0.05. (F–I) EGFP expression in gonad of dmrt1 promoter-driven EGFP transgenic medaka at 5 dph. During normal development, EGFP expression is detected only in male gonads (F,G), but not in female gonads (H). EGFP positive cells are observed in fasn XX G0 larva at 5 dph (I). Scale bars: 50 µm. Green arrowheads indicate EGFP expression in somatic cells. Green arrows indicate EGFP expression in germ cells. The rate of gonad which had EGFP positive gonadal somatic cells; (F) wild type (WT) XY (n=7/7). (G) fasn G0 larva XY (n=7/7). (H) WT XX (n=0/15). (I) fasn G0 larva XX (n=3/5).