Figure 3.
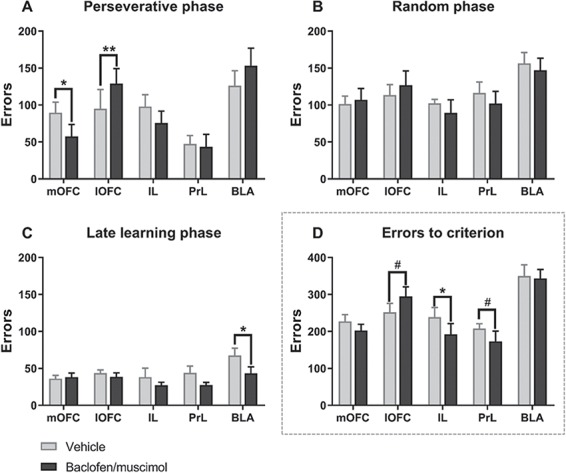
Effects of site-specific pharmacological inactivation on performance in deterministic touchscreen serial visual reversal task. (A–C) The effect of pharmacological inactivation on errors within each reversal learning phase: perseveration (A), random (B), and late learning (C). OFC inactivation affected only perseverative errors (A), with mOFC and lOFC exhibiting dissociable roles; inactivating the lOFC impaired, while mOFC inactivation improved, serial reversal learning performance as reflected by an increase and decrease in number of perseverative errors, respectively. (D) The effect of pharmacological inactivation on total errors to criterion of learning. Dissociable roles of the OFC and mPFC (IL and PrL) in deterministic serial visual reversal learning, as OFC inactivation affected only perseveration and mPFC inactivation affected learning overall. Results are represented as mean ± SEM; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05; #P < 0.1. Veh, vehicle; BM, baclofen/muscimol.
