Figure 1.
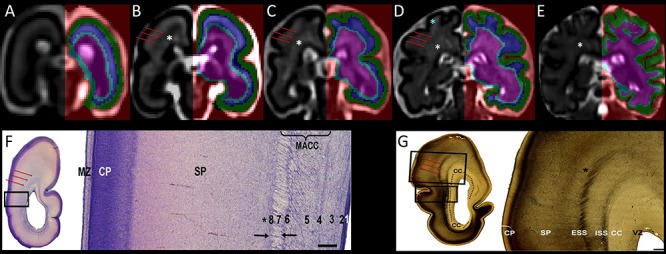
Coronal sections showing the segmentation of the telencephalic wall into transient fetal compartments (CP in green, SP in blue, and IZ with subcortical structures in light blue and pink) in 21.57 (A), 24.71 (B), 27.71 (C), 31.57 (D), and 34.14 (E) GW fetal brains. Transient fetal compartments were identified by using anatomical landmarks and the histological descriptions from Nissl (F) and AChE (G) stained sections (F and G were reproduced with permission from (Žunić Išasegi et al. 2018)). The superficial external sagittal stratum (red arrows) was used as a continuous border between the SP and the IZ. Note that the MR signal intensity varies within the SP (T2w hyperintense regions of the superficial SP within the gyral crowns are shown with blue asterisk) and the intermediate zone (periventricular crossroads are marked with the white asterisks (Judaš et al. 2005; Kidokoro et al. 2011; Girard et al. 2012). MACC, multilaminar axonal-cellular compartment; ISS, internal sagittal stratum; CC, corpus callosum; MZ, marginal zone; VZ, ventricular zone. VZ (1), inner subventricular zone (2), periventricular (callosal) fiber-rich zone (3), complex fibrillar/cellular stratum composed of the outer subventricular zone (OSVZ) and an inner (proliferative) cell layer (4–6), external sagittal stratum with strictly packed thalamocortical projection fibers (7), and external transient (proliferative) cell band (8) (descriptions reproduced with permission from (Žunić Išasegi et al. 2018)). Associative fibers along the border between the deep SP and the superficial IZ are marked with the black asterisks.
