Figure 1.
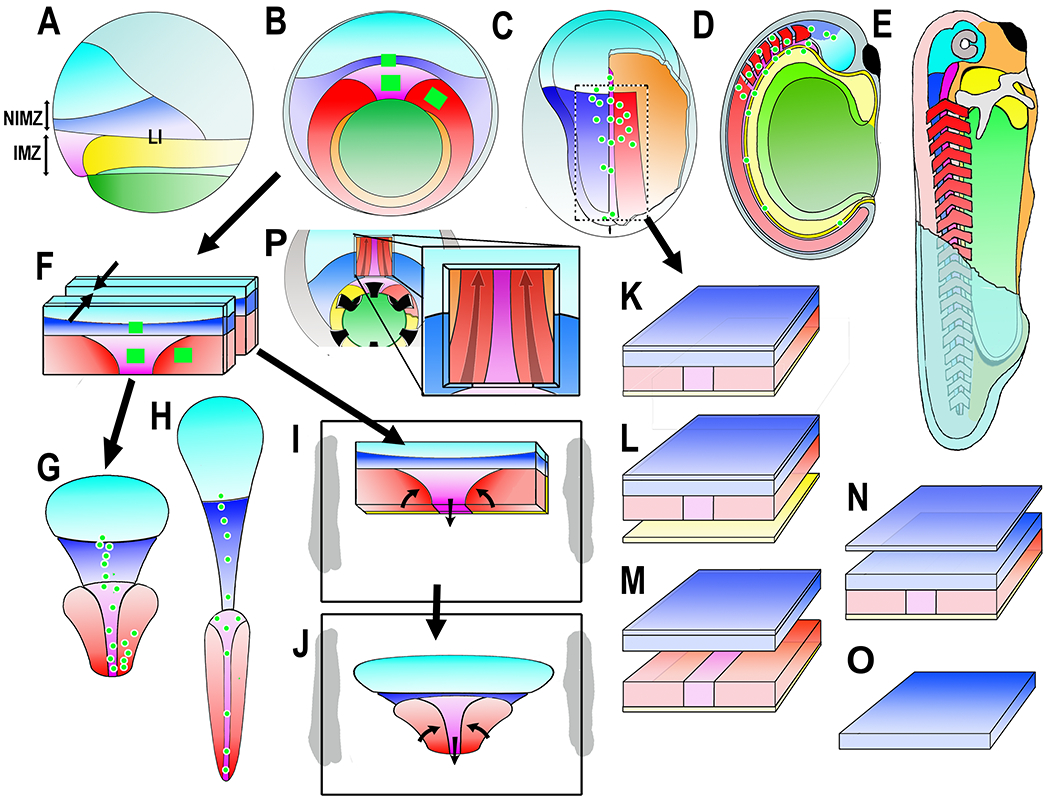
Diagrams show the Xenopus early gastrua fate map in lateral (A) and vegetal (B) views, the early neurula in dorsal view, right side cutaway to show postinvolution mesoderm (C), the closed neural tube stage in sagittal view (D), and the early tadpole in a cutaway view (E). Ectodermal fates are: epidermis (dull blue), forebrain (bright blue), and hindbrain/spinal cord (dark blue). Mesodermal fates are: notochord (magenta), somitic mesoderm (red), head, heart and lateroventral mesoderm (orange). Endodermal fates are: archenteron roof suprablastoporal endoderm (yellow, removed to show underlying mesoderm in B and explants (F-J), archenteron roof/bottle cell endoderm (light green), and vegetal endoderm (dark green). The future anterior-posterior (A-P) axes are shaded from A (dark) to P (light). Also indicated are the IMZ (Involuting Marginal Zone), the NIMZ (Non-Involuting Marginal Zone), and the LI (Limit of Involution). Construction of experimental preparations are shown for the “Keller Sandwich” (F-G-H), the Open-faced explant as made (F-I) and undergoing convergent extension (J), the “dorsal isolate” or “Wilson explant (C-K), with endodermal epithelium removed to reveal deep notochordal and somitic mesoderm (L), with neural and mesodermal separated to reveal their apposing surfaces (M), with epithelial neural removed to reveal deep neural with underlying mesoderm (N), and isolated neural deep layer (O), and the Davidson “windowed” embryo to reveal deep notochordal and somitic mesoderm (P). The square green patches and green dots are schematic representations of the graded separation of labeled patches of cells during convergent extension.
