Figure 2.
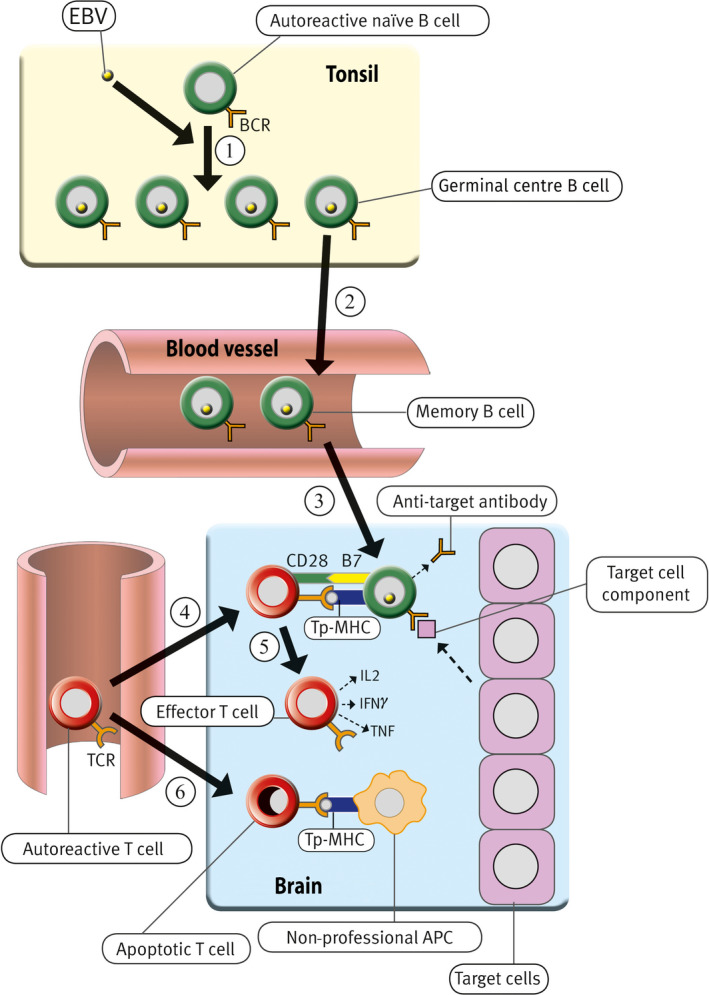
Proposed role of EBV infection in the development of BD. EBV infects autoreactive naïve B cells in the tonsil, driving them to proliferate and then enter germinal centres. In the germinal centres, they again proliferate and differentiate into latently infected autoreactive memory B cells (Step 1), which exit from the tonsil and circulate in the blood (Step 2). The number of EBV‐infected B cells is normally controlled by EBV‐specific cytotoxic CD8+ T cells, which kill the infected B cells. However, if there is a defective CD8+ T‐cell control of EBV infection, EBV‐infected cells survive and proliferate, resulting in an increased number of EBV‐infected autoreactive memory B cells that enter the brain where they lodge (Step 3). Circulating autoreactive T cells that have been activated in peripheral lymphoid organs enter the brain where they are reactivated by EBV‐infected autoreactive B cells presenting target cell peptides (Tp) bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules (Step 4). These EBV‐infected B cells provide costimulatory survival signals (B7) to the CD28 receptor on the autoreactive T cells and therefore inhibit the activation‐induced T‐cell apoptosis, which normally occurs when autoreactive T cells enter the brain and interact with non‐professional antigen‐presenting cells (APC) that do not express B7 costimulatory molecules 92 , 93 (Step 6). After the autoreactive T cells have been reactivated by EBV‐infected autoreactive B cells, they produce cytokines such as interleukin‐2 (IL‐2), interferon‐γ (IFN‐γ) and tumour necrosis factor (TNF) and orchestrate an autoimmune attack on the target cells, such as neurons expressing the NMDA receptor (Step 5). The autoreactive T cells also provide T‐cell help to the EBV‐infected autoreactive B cells that then differentiate into plasma cells. These plasma cells produce pathogenic autoantibodies, which attack target cell components, such as NMDA receptors. BCR, B‐cell receptor; TCR, T‐cell receptor. Modified from Pender 42 through a Creative Commons Licence.
