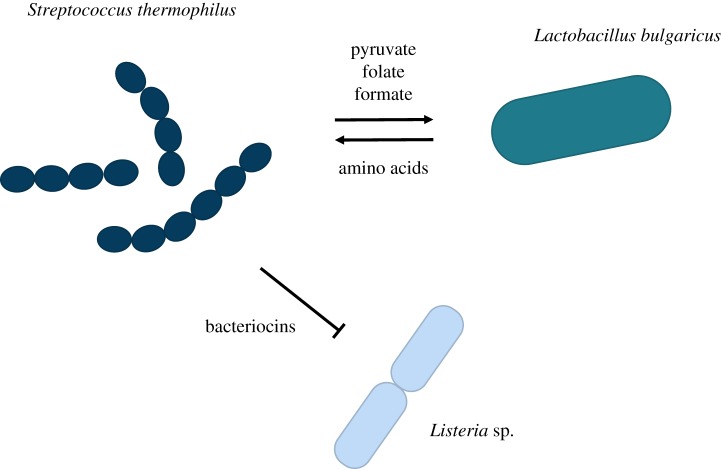
Figure 1.
Microbial communities are characterized by a multitude of often complex interactions between their members. For example, three bacterial species that can co-occur in dairy products engage in both positive and negative interactions, which are mediated by metabolic compounds and toxins [9,10]. (Online version in colour.)