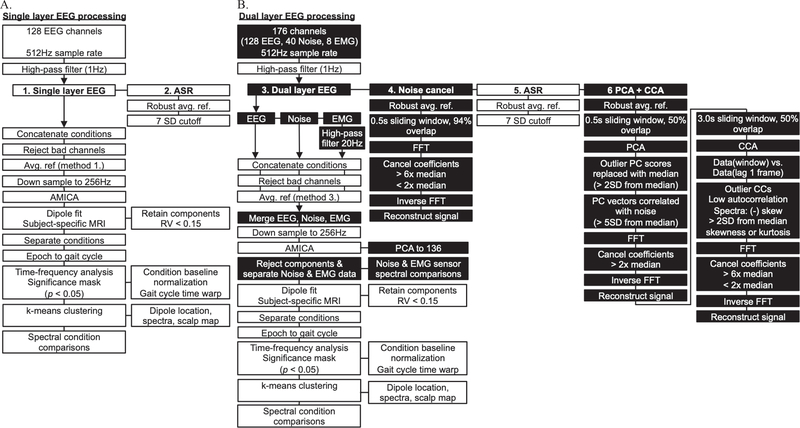
Figure 2.
Single (A.) and dual layer EEG (B.) processing pipelines. Common EEG processing steps (white boxes) and dual layer specific EEG processing steps (black boxes). Single-layer EEG approaches relied on 128-scalp EEG electrodes without additional preprocessing (1: Single layer EEG) and after Artifact Subspace Reconstruction (2: ASR). Dual-layer EEG approaches relied on 128-scalp EEG electrodes, 40 isolated noise-only electrodes, and 8 neck EMG electrodes merged into an adaptive mixture independent component analysis (AMICA) after contrasting preprocessing steps. Dual-layer EEG processing was completed without additional preprocessing (3: Dual layer EEG), after frequency domain noise cancellation (4: Noise cancel), after ASR (5), and after applying frequency domain noise cancellation to artifact components from principal component analysis and canonical component analysis (6: PCA+CCA).