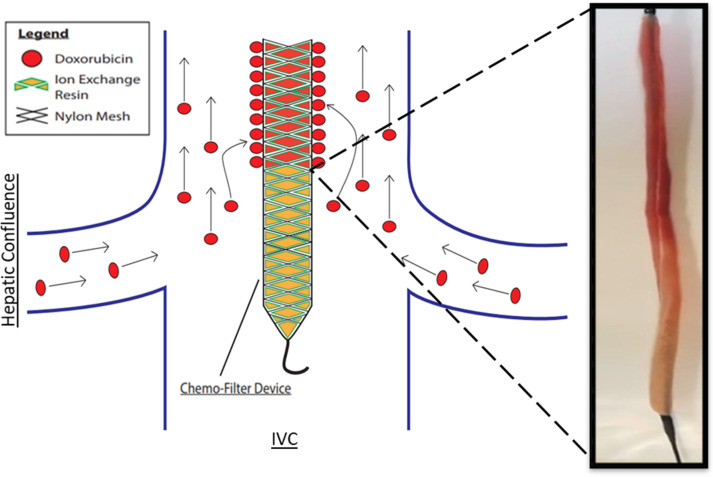
Figure 6a:
In situ doxorubicin (DOX) adsorption by the ChemoFilter (CF) device. (a) Schematic depicting in vivo DOX binding by CF device positioned adjacent to hepatic venous drainage. Prior to euthanasia, CF devices were retrieved through the jugular sheath and were washed with phosphate-buffered saline to remove adsorbed biomolecules. CF devices were viewed with a wide-field fluorescence microscope, and the fluorescence was used to detect DOX (red). Scale bars = 2 mm. (b) Distribution of filtered DOX (red) on CF devices relative to the hepatic venous outflow was observed (left side of image in b is equivalent to the cranial side in a). Enhanced DOX binding onto CF when positioned closer to the hepatic confluence. (c) Fluorescence microscopy was used to confirm DOX binding to strong acid cation ion exchange resin beads within the nylon sac. IVC = interior vena cava.