Figure 7. TAFI activity is required for CM’s inhibition of tPA-induced plasma clot lysis.
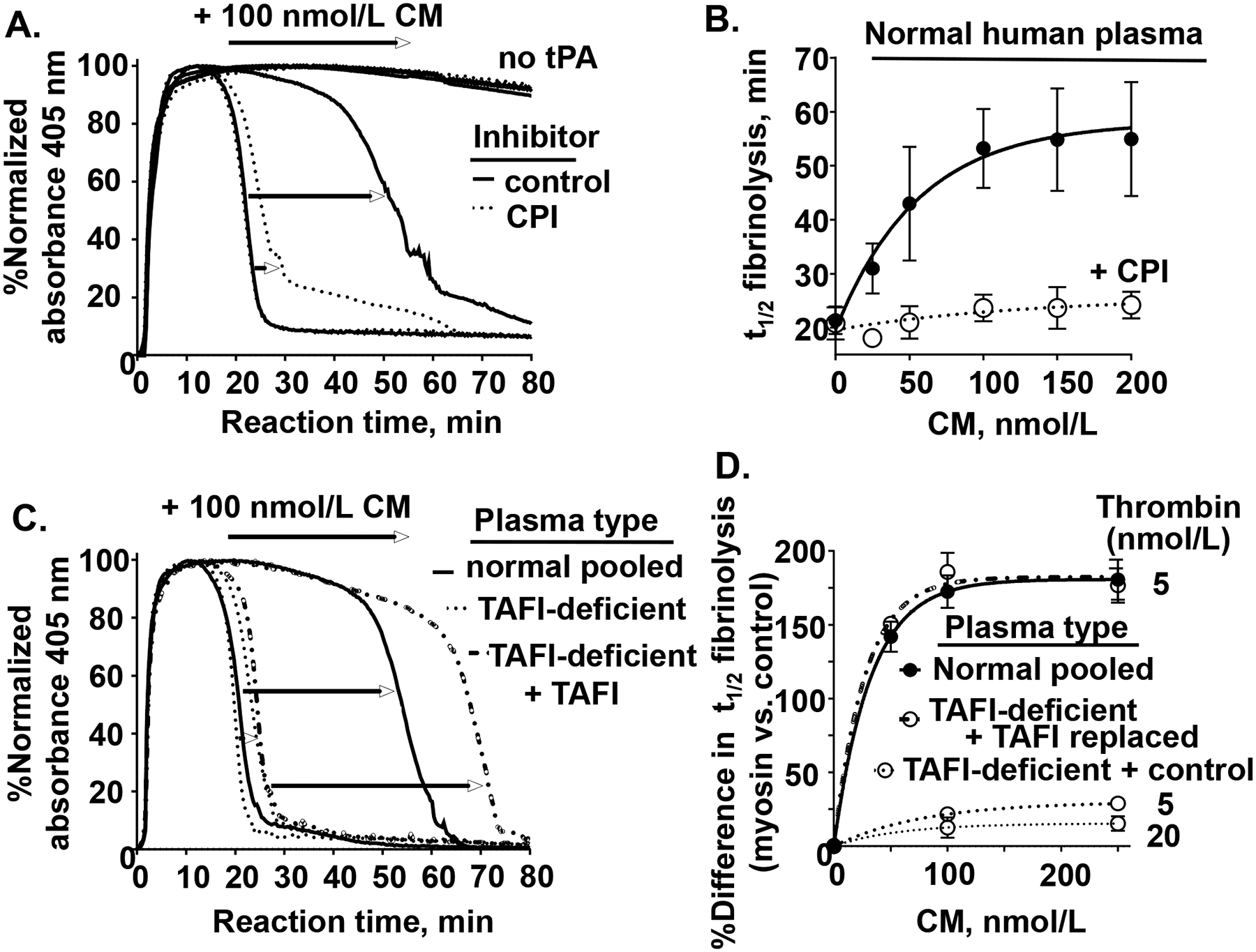
(A) Normal human pooled plasma was pre-incubated with either carboxypeptidase inhibitor (CPI) to inhibit TAFI (dotted lines) or control buffer (solid line) and clot lysis studies were done, as in Figure 6, with with 100 nmol/L CM and with 100 ng/mL tPA or without tPA (as indicated by “no tPA”). (B) Plasma clot lysis times (t1/2), determined as done in (A), were quantified in the presence of different levels of CM, 5 nmol/L thrombin, and 100 ng/mL tPA in the absence (●, solid line) or presence of the TAFIa inhibitor, CPI (○, dashed line). (C) TAFI-deficient plasma reconstituted with only control buffer or with reconsititued with normal levels of TAFI and normal plasma was used for plasma clot lysis studies (as above, using 5 nmol/L thrombin, and 100 ng/mL tPA) with either 0 or 100 nmol/L CM. (D) The percent difference in plasma clot lysis t1/2 between values for the presence of CM at the indicated concentrations (50, 100, 250 nmol/L) for the different indicated plasma types (normal (solid line), TAFI-deficient + control buffer (dotted lines for 5 nmol/L or 20 nmol/L thrombin), and TAFI-deficient + TAFI replacement (dash-dotted line)) are shown. Each value represents the mean [SD] of at least triplicate determinations.
