Extended Data Figure 6. Effect of VIPergic neuronal modulation with DREADDs on IL-22 production by CCR6+ ILC3.
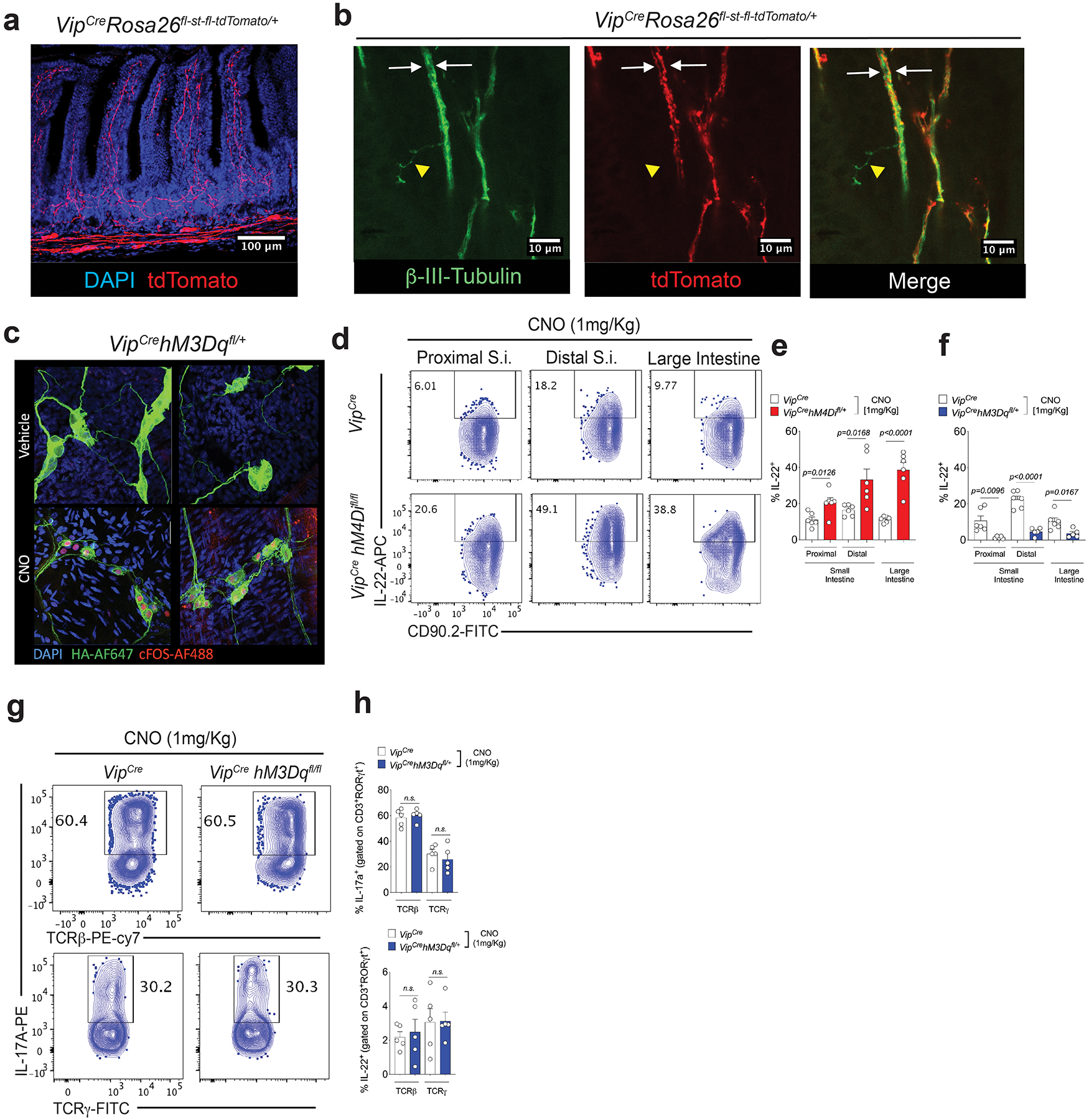
a, b, VIPCre activity in neurons in the gut. Homozygous VIPCre mice were bred to homozygous Rosa26fl-st-fl-tdTomato. (a) Distribution of tdTomato+ projections in the small intestine lamina propia. tdTomato: red; nucleus/Dapi: blue. (b) tdTomato positive and negative neurons present in the small intestine. tdTomato: red; pan=neuronal marker β3-tubulin: green. Two distinct β3-tubulin+ tdTomato+ neuronal projections (white arrows) can be observed in a bundle of enteric neurons in the villi. Yellow: β3-tubulin+ tdTomatonegative projection. c, Nuclear cFOS localization in VIPergic neurons 2h after CNO (1mg/Kg, i.p.) or vehicle treatment of mice expressing the DREADD for activation under the control of VIPCre (VIPCre hM3Dqfl/+). cFOS-AF488: red, hM3Dq-TA-AF647: green, Nucleus/Dapi: blue. d, e, f, Effect of chemogenetic modulation of VIPergic neurons on IL-22 production by CCR6+ ILC3 in the small intestine (S.I.) and large intestine (L.I.). Representative FACS plot (d) and summaries of IL-22 production by CCR6+ ILC3 in mice expressing the DREADD for inhibition (hM4Di) (e) and for activation (hM3Dq) (f). All the mice were treated with CNO (1mg/Kg, i.p, twice, 24h before sample collection). (e): n=6 mice/group. (f) VIPCre (n=6 mice/group) and VIPCrehM3DqCre : (n=5 mice/group). Mean ± SEM, two-sided t-test. g, h, No difference in the frequencies of IL-17 and IL-22 production by CD3+ RORγt +TCRγ+TCRβneg (γδT17) and CD3+ RORγt +TCRγnegTCRβ+ (Th17) cells after activation of VIPergic neurons. Representative FACS plot (g) and summaries (h) Mean ± SEM, two-sided t-test. n=5 mice/group. All the mice were treated with CNO (1mg/Kg, i.p, twice, 24h before sample collection).
