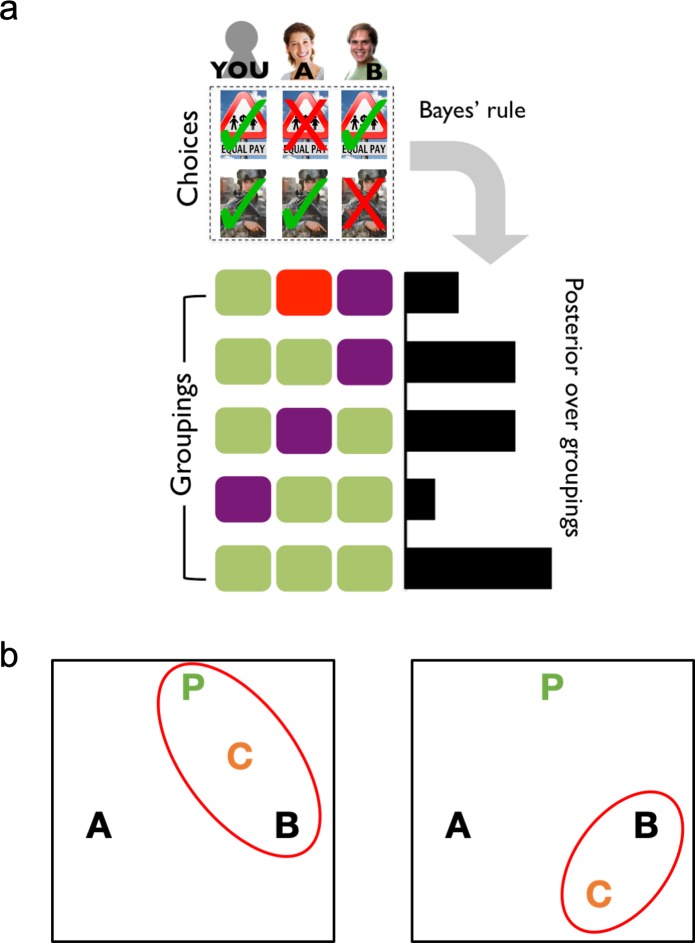
Figure 1. A formal account of social latent structure learning.
(A) Model schematic illustrating how choice patterns are transformed using Bayes’ rule to create a posterior over different possible latent groupings of agents. (B) Agents are represented as letters in an abstract space (P is the participant), where the distance between letters indicates the degree to which agents agree in their choices (i.e., choice overlap). Red ovals indicate the latent structures that have high posterior probability. Left: The placement of Agent C creates a cluster that includes both the participant and Agent B, which should increase estimates of Agent B as an ally. Right: The placement of Agent C excludes the participant from the cluster with Agents B and C, which should decrease estimates of Agent B as an ally.