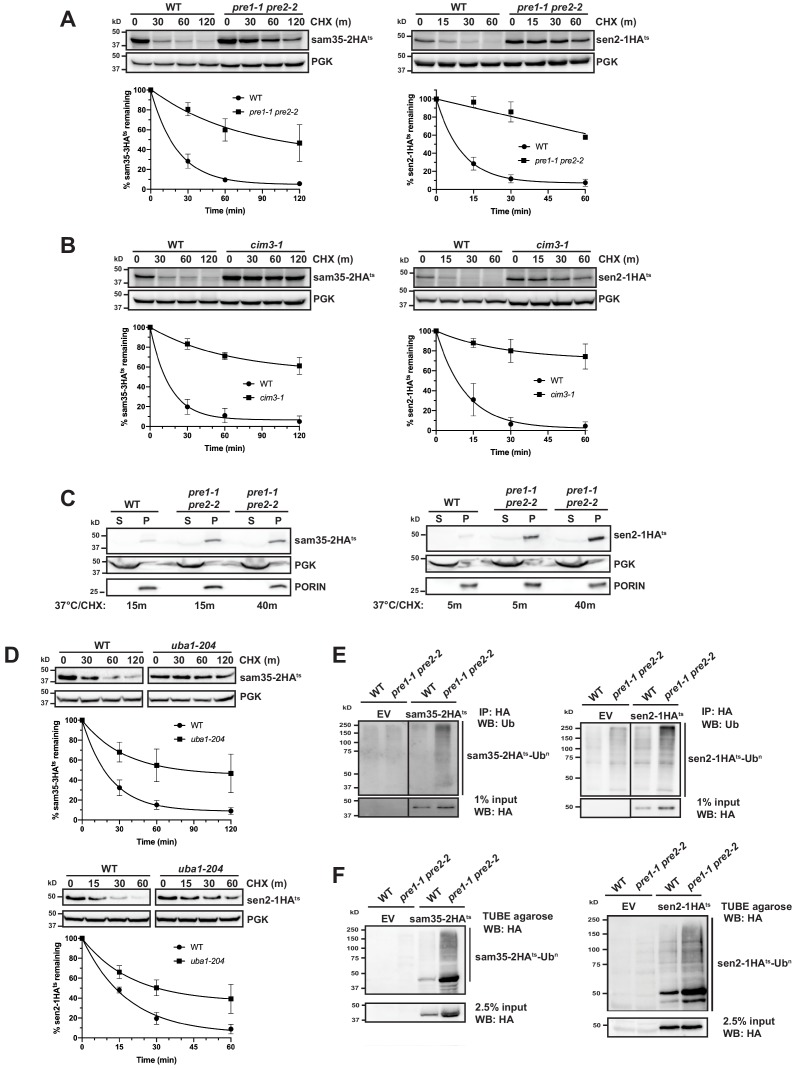
Figure 2. The degradation of MAD QC substrates requires the ubiquitin-proteasome system.
(A, B) CHX chase for the indicated times at 37°C assessing the turnover of sam35-2HAts or sen2-1HAts (pMM157 or 160, respectively) in WT (WCG4a) and pre1-1 pre2-2 proteasome mutant (WCG4-11/21a) cells (A) or WT (CIM) and cim3-1 proteasome mutant cells (B). Proteins were detected by immunoblotting. Graphed below is the mean and SD of the PGK-normalized HA signal at each time point for three biological replicates. (C) Lysates from the strains used in A were fractionated at 12,000xg into mitochondrial pellets (P) and post-mitochondrial supernatants (S) after incubation at 37°C for the indicated times. Fractions were subject to immunoblotting with antibodies to HA, PGK, and PORIN. (D) CHX chase for the indicated times at 37°C assessing the turnover of sam35-2HAts or sen2-1HAts (pMM157 or 160, respectively) in a uba1-204 strain relative to its isogenic WT strain. (E) Ubiquitination of sam35-2HAts and sen2-1HAts was assessed by immunoprecipitation (IP) from lysates of the strains used in A with anti-HA agarose, followed by immunoblotting with ubiquitin antibodies. 1% of IP input lysate was reserved and also analyzed by immunoblotting. (F) Ubiquitination of sam35-2HAts and sen2-1HAts was assessed by IP from lysates of the strains used in A using tandem ubiquitin-binding entities (TUBE) agarose, followed by immunoblotting with HA antibody. 2.5% of the TUBE input lysate was reserved and analyzed by immunoblotting.