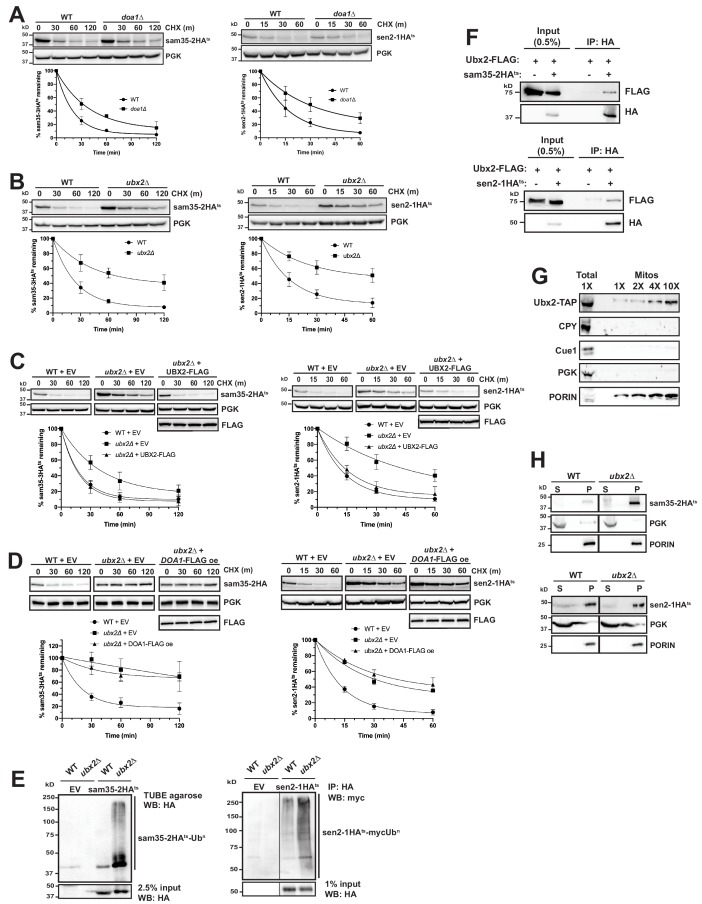
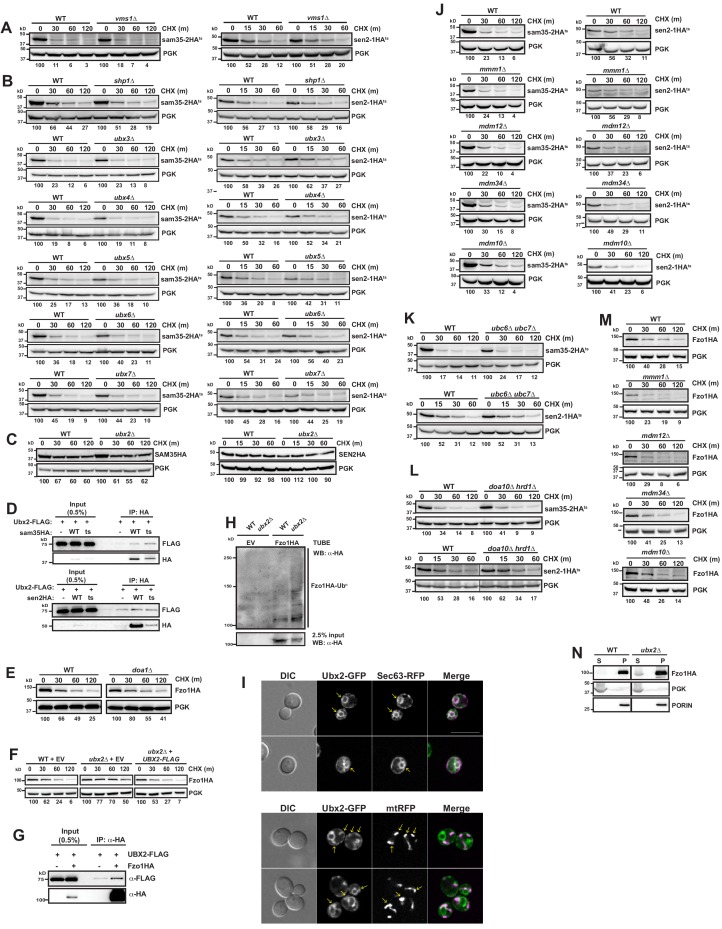
Figure 6. The Cdc48 co-factors Ubx2 and Doa1 are implicated in MAD.
(A) CHX chase for the indicated times at 37°C assessing the turnover of sam35-2HAts (pMM157) and sen2-1HAts (pMM160) in WT (BY4741) and doa1Δ cells (yJS208). Proteins were detected by immunoblotting. Graphed below is the mean and SD of the PGK-normalized HA signal at each time point for three biological replicates. (B) CHX chase as in A for the indicated times at 37°C assessing the turnover of sam35-2HAts (pMM157) and sen2-1HAts (pMM160) in WT (BY4741) and ubx2Δ cells (yJS155). (C) CHX chase as in A for the indicated times at 37°C assessing the turnover of sam35-2HAts (pMM157) and sen2-1HAts (pMM160) in WT (BY4741) and ubx2Δ (yJS155) cells co-expressing either empty vector (EV; pRS315) or CEN Ubx2-FLAG (pMM242). (D) CHX chase as in A for the indicated times at 37°C assessing the turnover of sam35-2HAts (pMM231) or sen2-1HAts (pMM234) in WT (BY4741) cells or ubx2Δ (yJS155) cells expressing either EV (pRS315) or Doa1-FLAG (pMM254) from a high copy 2μ plasmid. (E) Ubiquitination of sam35-2HAts and sen2-1HAts was assessed by IP using TUBE agarose or anti-HA agarose from ubx2Δ (yJS155) and WT (BY4741) lysates expressing EV (pRS315), sam35-2HAts (pMM157), or sen2-1HAts (pMM160), followed by immunoblotting with HA or c-myc antibody. 2.5% or 1% of the IP input lysate was reserved and analyzed by immunoblotting. (F) Co-IP of Ubx2-FLAG (pMM242) with sam35-2HAts or sen2-1HAts (pMM231 and 234, respectively) from pre1-1 pre2-2 (WCG4-11/21a) cells was assessed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. IP of Ubx2-FLAG from cells co-expressing EV (pRS316) in place of HA-tagged substrates and 0.5% of the input lysate are shown for comparison. (G) Lysate (‘Total’) and increasing amounts of mitochondria purified by 12,000xg and sucrose gradient fractionation (‘Mitos’) from Ubx2-TAP-expressing cells were examined by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (H) Lysates from WT (BY4741) and ubx2Δ (yJS155) cells expressing sam35-2HAts or sen2-1HAts (pMM157 and 160, respectively) were fractionated at 12,000xg at 37°C into mitochondrial pellets (P) and post-mitochondrial supernatants (S). Fractions were subject to immunoblotting with antibodies to HA, PGK, and PORIN.