Figure 4. P2X4 deficiency attenuates kidney apoptosis after ischemic AKI.
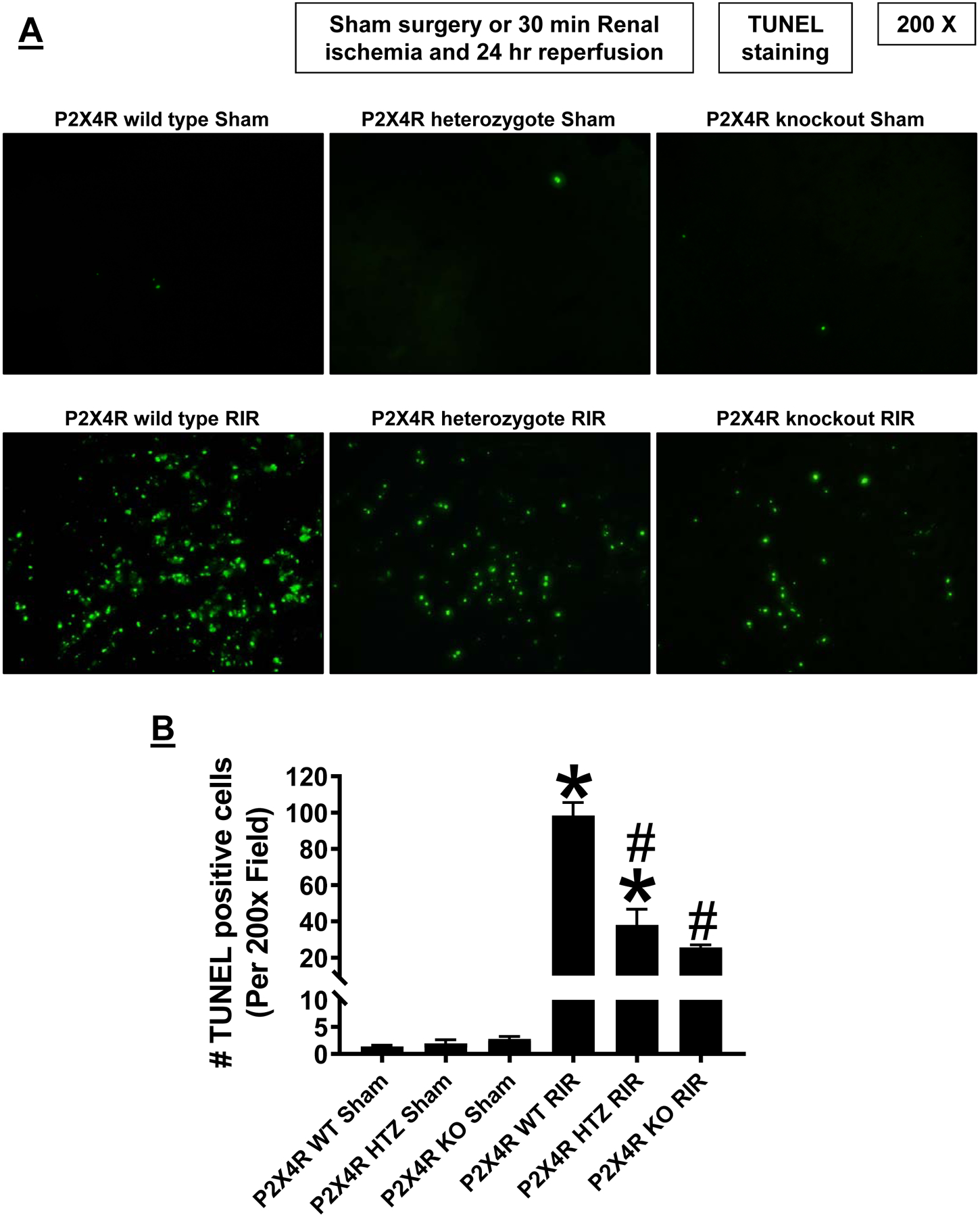
A. Representative images of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase biotin-dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining indicative of renal tubular apoptosis and counts of TUNEL positive kidney cells (B) in the kidneys of P2X4 wild type (WT), P2X4 heterozygous (HTZ) and P2X4 deficient (KO) mice subjected to sham-surgery (N=3) or to 30 min renal ischemia and 24 hr reperfusion (IR, N=5–7 magnification 200X). *P<0.05 vs. P2X4 WT mice subjected to sham surgery. #P<0.05 vs. P2X4 WT mice subjected to renal IR. Error bars represent 1 SEM. For statistical analysis, the one-way ANOVA plus Tukey’s post hoc multiple comparison test was used to detect significant changes.
