Figure 7. P2X4 antagonism with 5-BDBD protects against renal IR injury in mice.
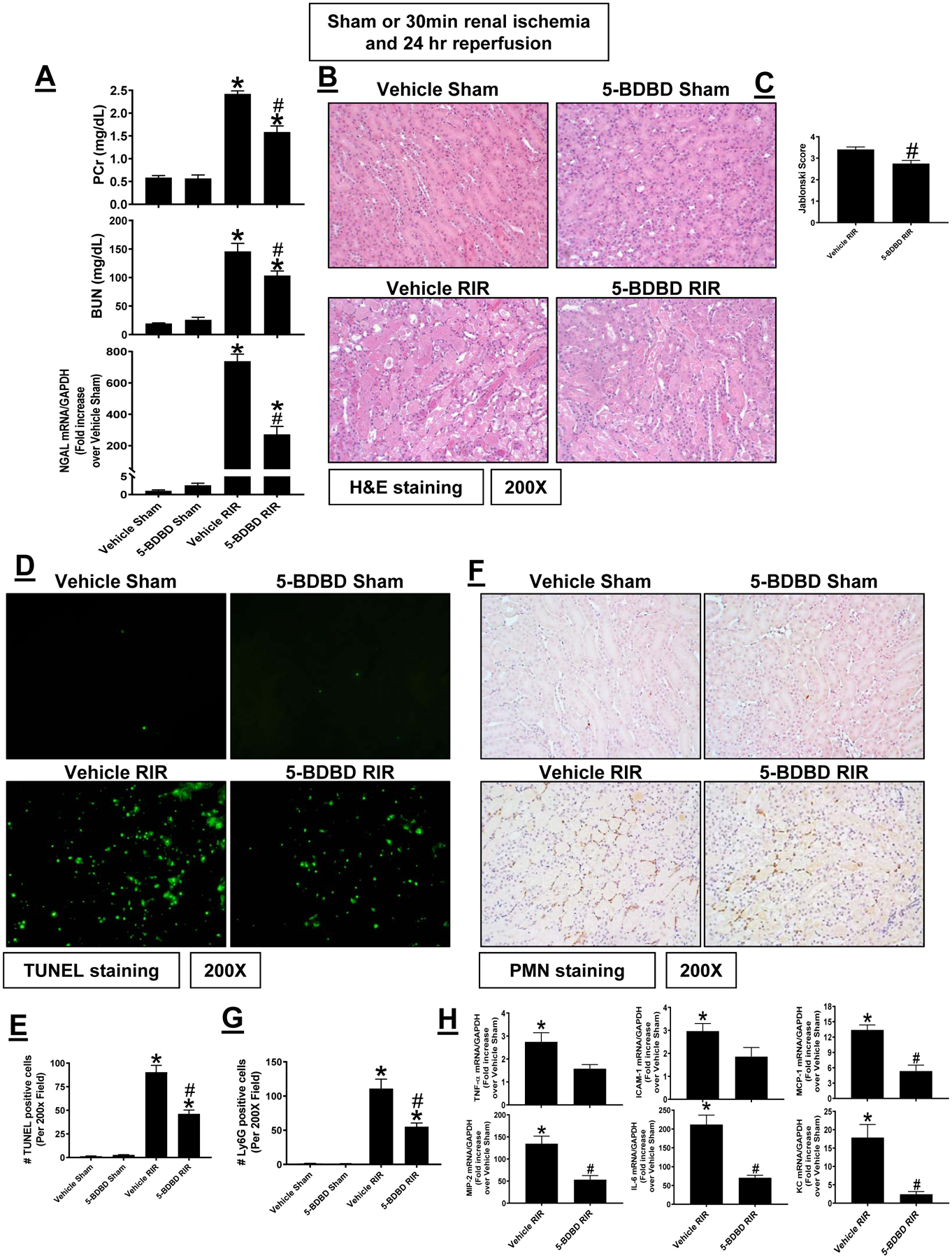
Wild type mice were treated with vehicle (intralipid 20%) or with 5-BDBD (a selective P2X4 antagonist, 1 mg/kg 30 min before surgery) and subjected to sham-surgery or to 30 min renal ischemia and 24 hr reperfusion (IR, N=5–6). 5-BDBD treatment reduced renal injury measured by plasma creatinine, BUN and kidney NGAL mRNA expression (A), renal tubular necrosis (B and C), renal tubular apoptosis (D and E), neutrophil infiltration (F and G) and kidney cytokine mRNA induction (H). TUNEL and neutrophil immunohistochemistry show 200X magnification images. For RTPCR, fold increases in pro-inflammatory mRNAs normalized to GAPDH from quantitative RT-PCR reactions for each indicated mRNA are shown. *P < 0.05 vs. P2X4 WT sham-operated mice. #P < 0.05 vs. P2X4 WT mice subjected to renal IR injury. Error bars represent 1 SEM.
