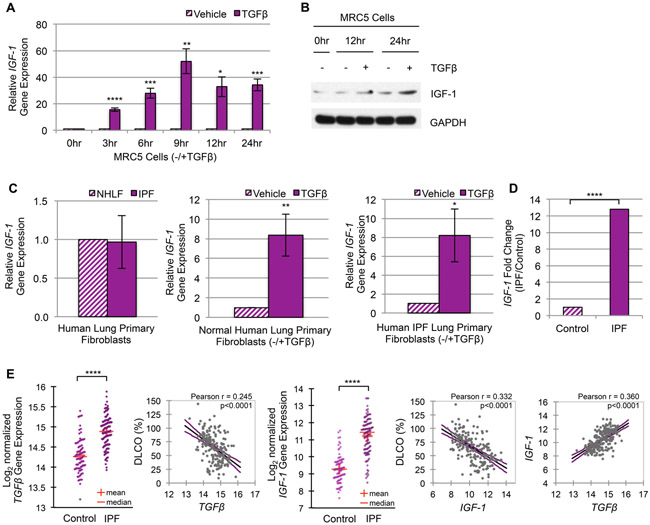
Figure 3. TGFβ upregulates IGF-1 in human fibroblasts and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.
(A) RT-qPCR of IGF-1 gene expression in MRC5 human lung fibroblasts treated with TGFβ or vehicle for the indicated times (n=3). (B) Western blot of cellular IGF-1 protein synthesis in MRC5 cells subsequent to TGFβ (+) or vehicle (−) treatment (n=3). (C) RT-qPCR of IGF-1 gene expression in Normal Human Lung Primary Fibroblasts (NHLF, n=5) compared to Human Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Primary Fibroblasts (IPF, n=4) after 24 hours growth (left panel) or following 24 hours stimulation with TGFβ or vehicle (middle and right panels). (D) Differential IGF-1 gene expression analysis of RNA-seq data from RNA isolated from whole lung tissue of control (n=8) and IPF (n=8) patients. IGF-1 ranked the 6th most upregulated gene of 2,560 total genes in this small cohort of Mayo Clinic patients. (E) Differential TGFβ (panel 1) and IGF-1 (panel 3) gene expression from microarray data of RNA isolated from whole lung tissue of control (n=91) and IPF (n=122) patients from a published study by the Lung Genomics Research Consortium (LGRC) under accession number GSE47460. IGF-1 ranked the 29th most upregulated gene of 15,261 total genes. Linear regression plots with 95% confidence interval and Pearson’s correlation coefficient of the LGRC patient cohort illustrate the correlation between TGFβ and %DLCO (panel 2), IGF-1 and %DLCO (panel 4), or IGF-1 and TGFβ gene expression (panel 5). The level of fibrosis is determined by decrease in pulmonary function (measured by the percentage of predicted diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide, % DLCO). Data are presented as means −/+ Standard Error of the Mean (SEM) for the number of biological replicates indicated (n). Statistical significance was determined after computing single factor ANOVA and/or unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test (p<0.05 (*), p<0.01 (**), p<0.005 (***), p<0.001 (****). Results demonstrate that (1) TGFβ promotes IGF-1 gene expression and/or ligand production in human lung fibroblast cell lines and primary human lung fibroblasts; and (2) IGF-1 levels correlate with decreased pulmonary function and increased TGFβ expression.