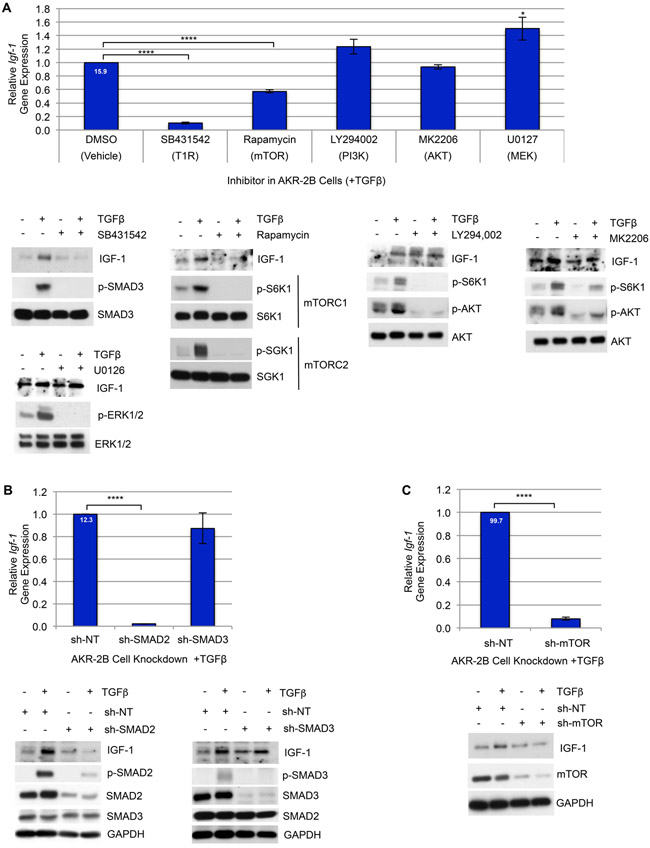
Figure 6. TGFβ-dependent induction of Igf-1 is mediated by SMAD2 & mTOR signaling.
(A) Top: RT-qPCR of Igf-1 gene expression in AKR-2B cells pre-treated for 2 hours with the indicated TGFβ-pathway inhibitors (10 μM SB431542, TGFβ Type-I Receptor (T1R) inhibitor; 20 μM LY294002, PI3K inhibitor; 300 nM MK2206, AKT inhibitor; 10 μM U0126, MEK inhibitor; 10 nM Rapamycin, mTOR inhibitor) or vehicle (0.1% DMSO), followed by stimulation with TGFβ for 12 hours (n=4). Bottom: Western blot of IGF-1 in AKR-2B cells as treated for qPCR and controls show the functionality of inhibitors on target protein activation following 3 (p-ERK/ERK) or 6 hours (p-SMAD3/SMAD3, p-AKT/AKT, p-S6K/S6K, p-SGK1/SGK1) treatment (n=3). (B) Top: RT-qPCR of Igf-1 expression in AKR-2B cells with shRNA-mediated stable knockdown of SMAD2 (sh-SMAD2), SMAD3 (sh-SMAD3), or nontargeting (sh-NT) after 12 hours TGFβ stimulation (n=3). Bottom: Western blot of IGF-1 in AKR-2B KD cells as treated for qPCR and controls confirming the level of knockdown of SMAD2, SMAD3, and p-SMAD2 or p-SMAD3 at 6 hours with TGFβ (+) or vehicle (−) (n=3). (C) Top: RT-qPCR of Igf-1 gene expression in AKR-2B cells with shRNA-mediated stable knockdown of mTOR (sh-mTOR) or NT (sh-NT) following 12 hours TGFβ stimulation (n=4). Bottom: Western blot of IGF-1 in AKR-2B KD cells as treated for qPCR and controls confirm the level of mTOR KD at 6 hours in the presence or absence of TGFβ (n=3). (A-C) Relative fold gene expression by TGFβ compared to control is indicated at the top of the vehicle or NT bars. Data are presented as means −/+ Standard Error of the Mean (SEM) for the number of biological replicates indicated (n). Statistical significance was determined after computing single factor ANOVA and/or unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test (p<0.05 (*), p<0.01 (**), p<0.005 (***), p<0.001 (****). Results demonstrate that TGFβ-induction of Igf-1 transcription and translation requires SMAD2 & mTOR signaling.