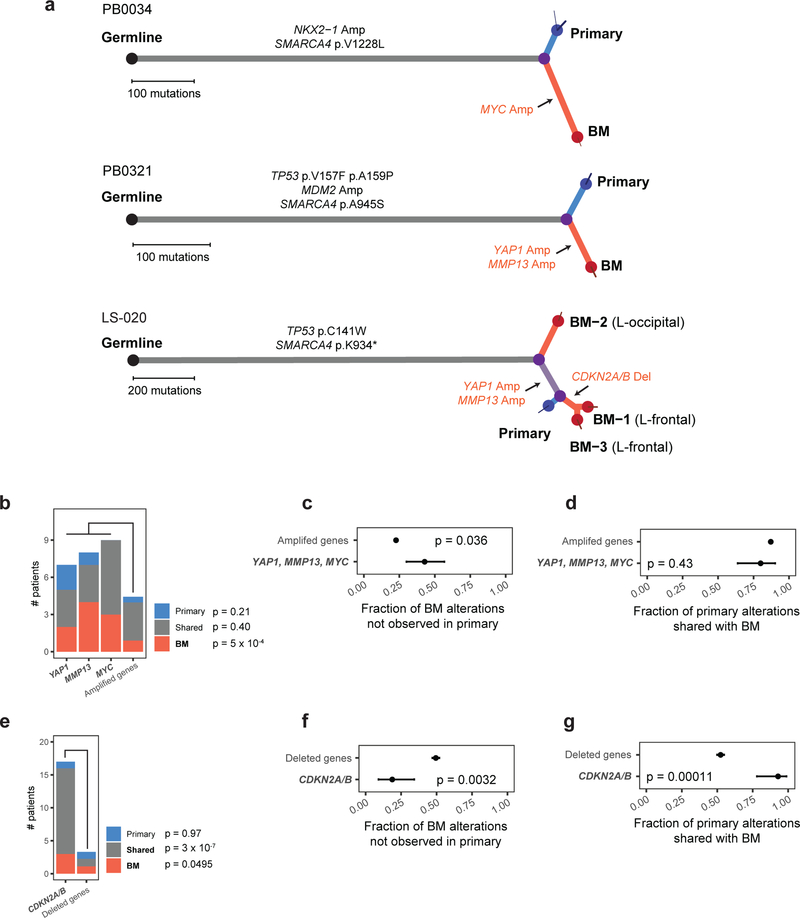
Fig. 3: Phylogenetic analysis of copy-number drivers in brain metastasis and matched primary tumors.
a, Somatic mutations in BM-LUAD cases bearing candidate drivers, depicted as phylogenetic trees. Branch lengths are proportional to the number of somatic point-mutations incurred along each lineage. Thin terminal branches indicate subclones with estimated cancer cell fraction less than 1.0 in the indicated sample. Somatic alterations in genes considered significantly recurrently mutated in TCGA-LUAD by CNA or mutation are annotated in black on the indicted phylogenetic branch. Somatic amplification and deletion of proposed candidate driver genes are indicated in red. b, Frequency of high-level amplifications that were private to the primary tumor, private to brain metastasis, or shared. The ‘other amplified gene’ column represents the average number of samples the other recurrently amplified genes were amplified in. Significance was determined using Poisson regression and Wald test. c, Fraction of high-level amplifications in brain metastases that were not detected in paired primary tumors. Significance was determined using Fisher’s exact test. Error bars represent 80% confidence intervals. d, Fraction of high-level amplifications in primary-tumor samples that were also detected in paired brain metastases. Significance was determined using Fisher’s exact test. Error bars represent 80% confidence intervals. e, Frequencies of deletions that were private to the primary tumor, private to brain metastasis, or shared. The ‘other deleted gene’ column represents the average number of samples the other recurrently deleted genes were deleted in. Significance was determined using Poisson regression and Wald test. f, Fraction of deletions in brain metastases that were not detected in their paired primary tumors. Significance was determined using Fisher’s exact test. Error bars represent 80% confidence intervals. g, Fraction of deletions in primary-tumor samples that were also detected in paired brain metastases. Significance was determined using Fisher’s exact test. Error bars represent 80% confidence intervals.