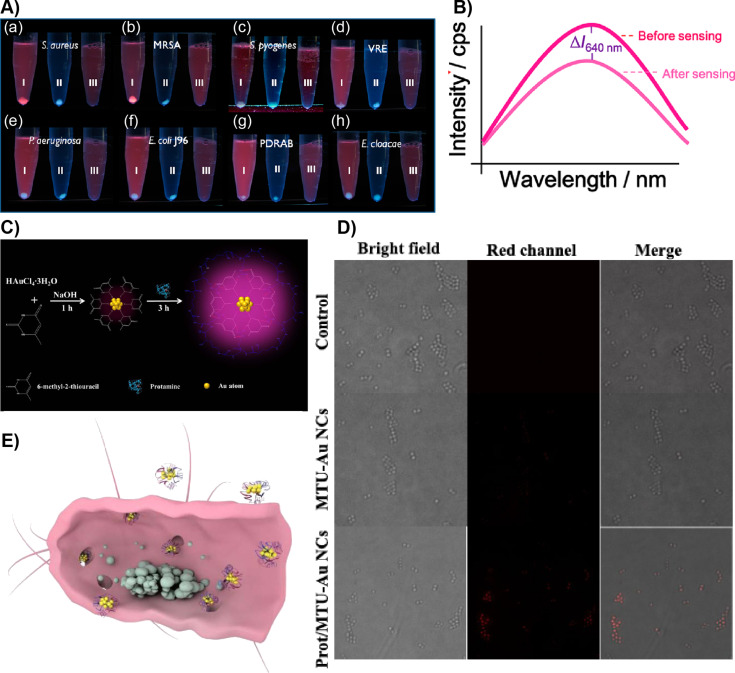
Figure 2.
AuNC-based pathogen sensing and imaging. A) (a–h) Photographs showing the sensing of various pathogenic bacterial strains after incubating them with 0.12 mg/mL of Au-HSA NCs followed by centrifugation at 3500 rpm (tubes labeled as “I”) in PBS buffer at pH 6.0. Tubes labeled as “II” in each panel contained only bacteria. Tubes labeled as “III” in each panel show the solution containing only Au-HSA NCs. B) Fluorescence spectra showing a change in the fluorescence intensity at 640 nm of Au-HSA NCs after bacterial sensing. C) Schematic representation of Au-MTU/Prot NC synthesis. D) Microscopy images of S. aureus after treatment with Au-MTU/Prot NCs, Au-MTU/Prot NCs, and control. The red channel was excited at 405 nm. The images were 40 μm × 40 μm. E) A cross-sectional schematic view of a bacterium treated with Au-MTU/Prot. Figure panel 2A is adapted and panel 2B is reused with permission from [83], copyright 2012 American Chemical Society. Figure panels 2C–E are reused with permission from [84], copyright 2019 Americal Chemical Society.