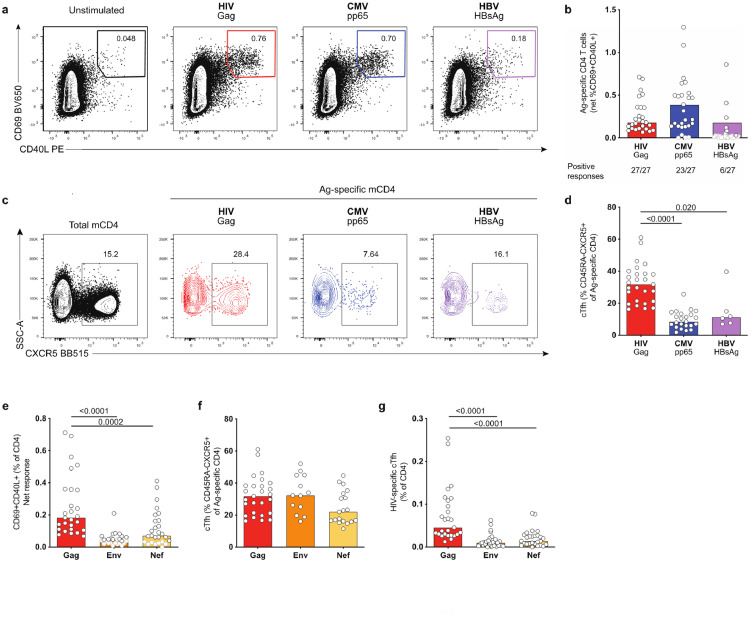
Fig. 1.
HIV-specific cTfh are expanded compared to CMV- and HBV-specific cTfh in ART-treated donors. PBMCs were stimulated for 9 h with peptide pools for HIV Gag, CMV pp65, HBV HBsAg or left unstimulated. Ag-specific CD4+ T cells were identified by the concurrent upregulation of CD40L and CD69 (AIM+ cells). (a) Example plots showing gating for CD69+CD40L+ for one representative donor (pre-gated on CD4+). (b) Net frequency of AIM+ Ag-specific CD4+T cells. Responses greater than 2-fold over background are shown as black bordered circles, responses below this threshold are shown as gray-bordered symbols. Median values shown were calculated using responses greater than 2-fold over background only. Below each bar, numbers of individuals with positive responses for each antigen are shown. (c) Example plot showing gating of cTfh as memory CD4+ T cells expressing CXCR5. Left hand panel shows gating on total memory CD4+(black). Ag-specific memory CD4+ T cells are shown as colored plots. (d) Quantification of results in (c). (e) Net frequency of HIV-specific CD4+ T cell responses identified using AIM assay. (f) Frequency of cTfh (CXCR5+) within HIV-specific CD4+ T cells (g) Frequency of HIV-specific cTfh of total CD4+ T cells. n = 27 for (b), (e) and (g); for (d): HIV Gag: n = 27, CMV pp65: n = 23, HBV HBsAg n = 6; for (f): HIV Gag: n = 27, Env: n = 13, Nef: n = 19. Bars represent median values. Only significant p-values are shown and were calculated by Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn's post test. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)