Figure 3: Proposed evolution of cellular immune effector lineages.
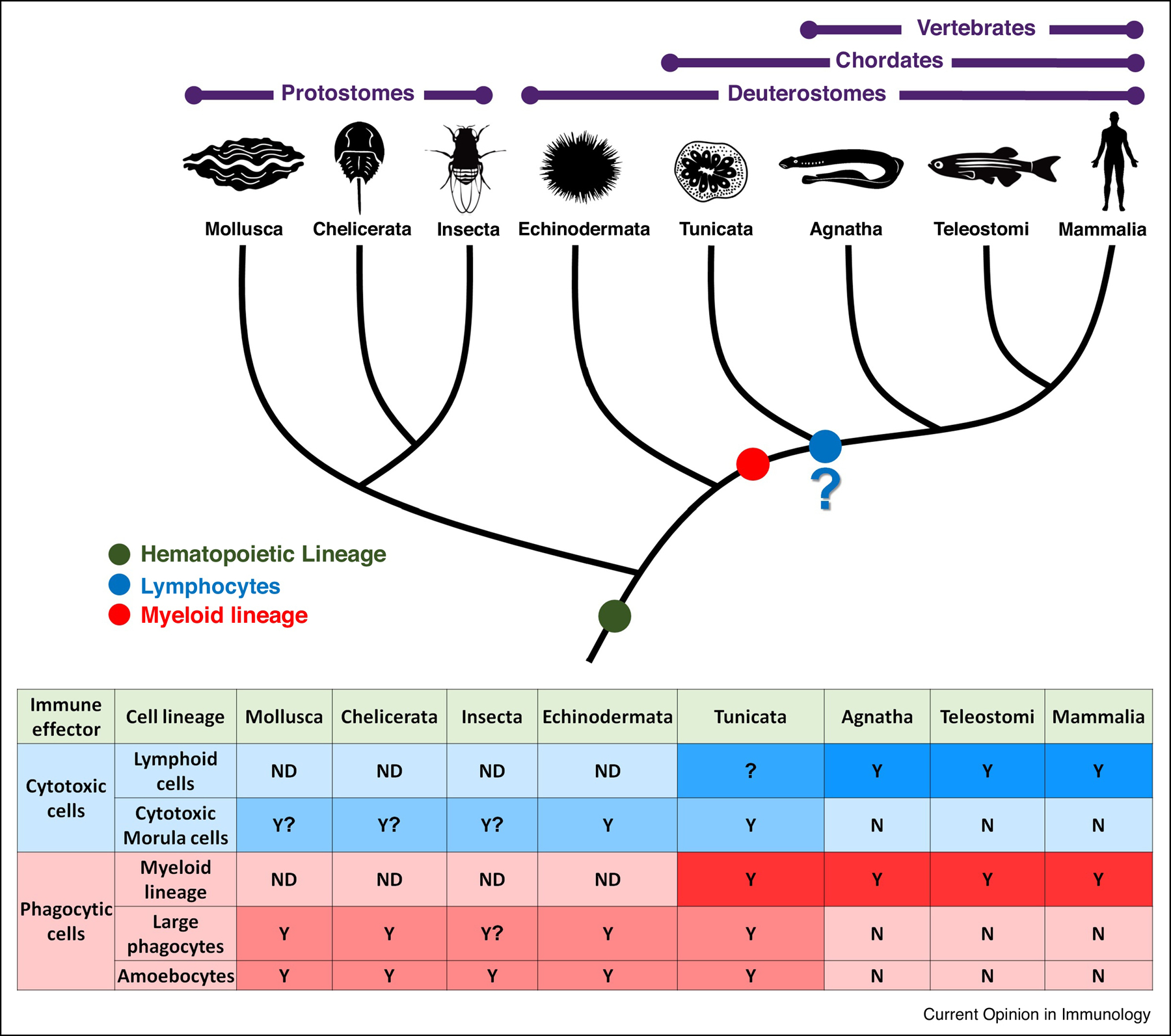
Proposed evolutionary perspective of the cellular immune system, mainly cytotoxic and phagocytic cell lineages. Table at the bottom describes the type of presumed immune associated cells found in each animal group. It appears that myeloid lineage evolved before the branching of the vertebrata from tunicates (red). Amoebocytes and large phagocytes can be found in B. schlosseri and other invertebrate species (light red). While there are some populations and molecular markers resembling lymphoid lineage, whether this lineage evolved in the common ancestor of tunicates and vertebrates is still to be deciphered (blue). On the other hand the cytotoxic morula cells are characterized in tunicates and likely exist in other invertebrates (light blue).Y- Yes, cell lineage present, N- cell lineage Not present, ND- No data, “?”- insufficient data (adopted from 22).
