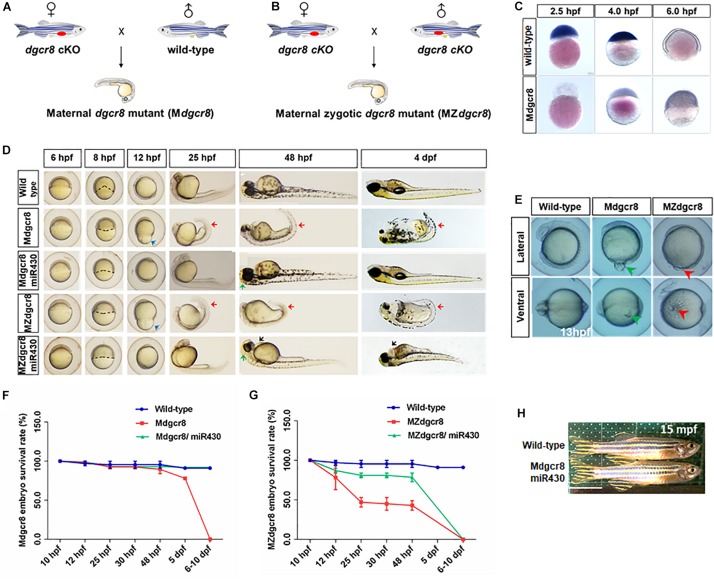
FIGURE 2.
Rescue of Mdgcr8 and MZdgcr8 using miR-430 duplex. (A) A schematic diagram of generating Mdgcr8 mutant zebrafish by out-crossing with wild-type male. (B) A schematic diagram of generating MZdgcr8 mutant zebrafish by in-crossing. (C) The expression of dgcr8 was analyzed by in situ hybridization in early embryonic stage. (D) Mdgcr8 and MZdgcr8 exhibit gastrulation defect, brain malformations, body curvature, and heart developmental defects compared with wild-type. miR-430 duplex was used to rescue the defects. (E) Epiboly defects in Mdgcr8 and MZdgcr8. At 14 hpf, the phenotype of yolk excision could be observed in MZdgcr8 mutant (5 X), but not in Mdgcr8. (F) Mdgcr8 embryonic survival rate become normal after rescue. (G) MZdgcr8 mutant embryos only survived up to 6–10 dpf after rescue. (H) Mdgcr8 mutant embryos after rescue could develop to adults and exhibit proper sex ratio. Scale bar 1 cm.