FIGURE 7.
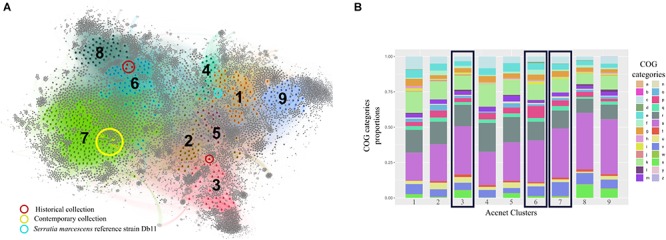
Clustering and analysis of the categorical functions of the accessory genome of the studied Serratia marcescens isolates (n = 8) and the 444 publicly available genomes by AcCNET software. (A) AcCNET pangenome network with detected clusters (n = 9) highlighted by colors and numbers. Colored and gray dots correspond to genomes and annotated proteins respectively and are linked by edges. Strains from our collections and the reference genome for S. marcescens species (Db11 strain, assembly accession GCA_000513215.1) are highlighted. (B) Accessory genome functional analysis of the nine detected clusters based on COGs proportions. Black rectangles depict the clusters where strains from our collections belong to. a, RNA processing and modification; b, chromatin structure and dynamics; c, energy production and conversion; d, cell cycle, control, mitosis; e, amino acid metabolism and transport; f, nucleotide metabolism and transport; g, carbohydrate metabolism and transport; h, coenzyme metabolism; i, lipid metabolism; j, translation; k, transcription; l, replication and repair; m, cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis; n, cell motility; o, post-translational modification, protein turnover, chaperon functions; p, inorganic ion transport and metabolism; q, secondary structure; r, general function prediction only; s, function unknown; t, signal transduction; u, intracellular trafficking and secretion; v, defense mechanisms; W, extracellular structures; x, mobilome, prophages, and transposons-related proteins; y, nuclear structure; z, cytoskeleton.
