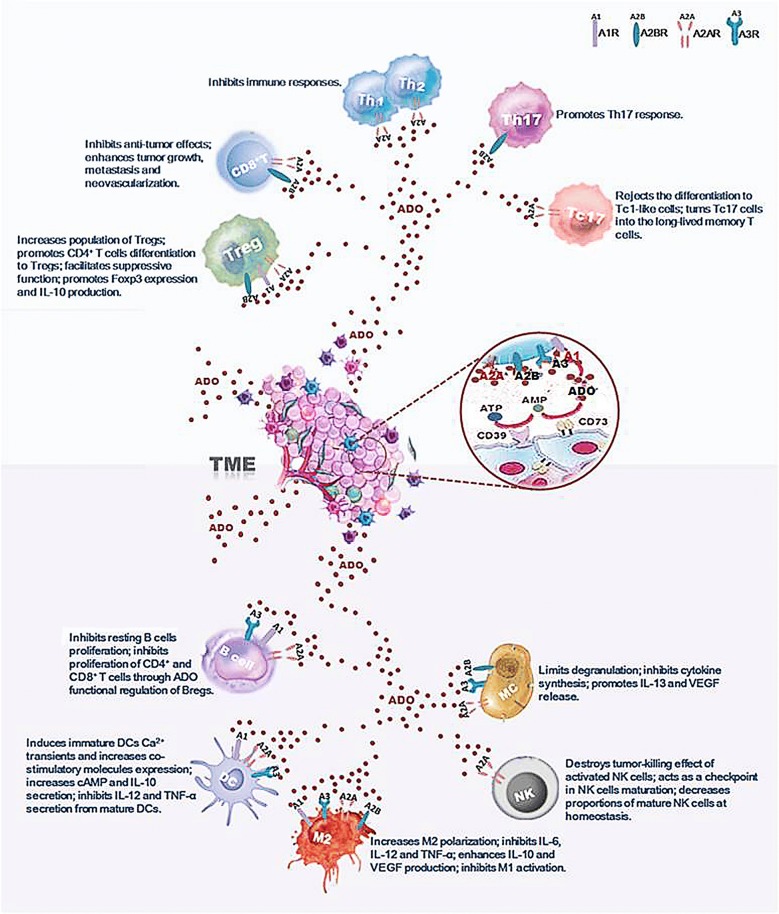
Fig. 2.
Extracellular adenosine (ADO) at a high concentration (over 100 μM) conducted immune-suppressive functions through activation of different ADO receptors on immune cells in tumor microenvironment (TME). For T cells in TME, ADO not only decreases anti-tumor function of CD8+ T cells, Th1 cells and Th2 cells but also enhances the function of regulatory T cells (Treg), Th17 cells and Tc17 cells. ADO also affects B cells, dendritic cells (DCs), mast cells (MCs), natural killer (NK) cells and macrophages (Mø) functions in anti-tumor immunity