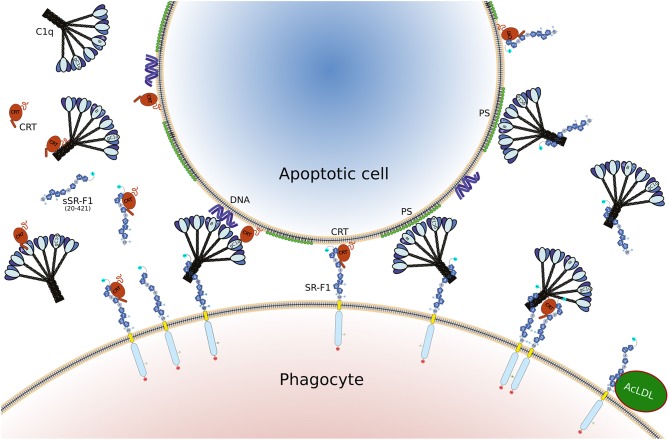
Figure 8.
Illustration of the different interactions involving SR-F1, C1q, CRT, and AcLDL, as discussed in the present article. The full length SR-F1 includes 7 EGF like domains (dark blue pentagons numbered 1, 2, 4, 6–9), 3 EGF repeats containing domains (small medium blue pentagons numbered 3, 5, 10), a transmembrane domain (yellow) and a cytosolic domain (light blue). The N- and C-terminal extremities of SR-F1 are indicated by a cyan and red circle, respectively, and the N-linked glycans by a circled N. Soluble forms of SR-F1 extracellular domain (sSR-F1) are also shown but for the sake of simplicity only the soluble SR-F1(20-421) form has been depicted. In the center, possible phagocyte-apoptotic cell interactions mediated by SR-F1 are shown. On the left and on the right, molecular interactions interfering with the phagocyte-apoptotic cell interaction involving soluble CRT and sSR-F1, respectively. On the lower right, the SR-F1-AcLDL complex is shown as well as a putative hetero-tetramer in which soluble CRT may enhance anchoring of C1q to SR-F1 and SR-F1 clustering with possible consequences on phagocyte-apoptotic cell interactions.