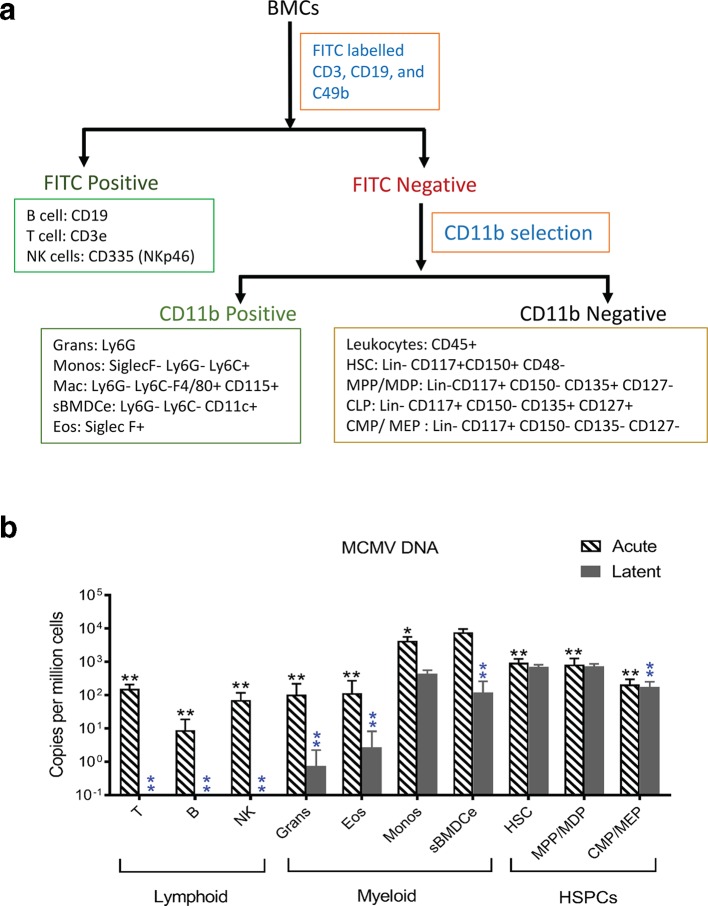
Fig. 6.
Identification of cell types that harbour viral DNA in haematopoietic BMCs in acutely and latently infected mice. Freshly isolated BMCs from acutely infected (day 5 p.i.) and latently infected mouse BM (3 months p.i.) were initially separated into three fractions using magnetic beads as described in Methods. Each of these three cell fractions was then stained with antibody panels (Table S3), and sorted by flow cytometry. Using this gating strategy (Fig. S3), ten major subsets of cells were collected. Genomic DNA samples from these sorted BMCs (sBMCs) were used to quantify MCMV DNA via qPCR. (a) Sorting strategy of haematopoietic BMCs. BMCs were firstly separated into FITC positive (lymphoid cells) and FITC negative (non-lymphoid cells) populations with mouse FITC positive selection magnetic beads, then the FITC negative cells were separated with CD11b selection magnetic beads into CD11b+ (myeloid cells) and CD11b- (HSPCs) populations. These three populations of cells were stained with antibodies listed in Table S4, and were sorted based on the combination of cell-surface markers shown in Fig. S4. (b) Quantification of viral DNA in sorted BMCs. DNA was extracted from each population of cells, and subject to qPCR with Taqman primers and probe specific to the MIEP region of the MCMV genome. The quantity of the MCMV genome was normalized against cellular gene mEF1α, and then converted to copy number per million cells. Values for naïve mice were set to zero and infected mice shown relative to naïve mice. BMCs from five mice were pooled and considered a biological replicate indicated by ‘N’. For infected mice N≥3, for uninfected controls N≥2. Data are presented as mean±sd. Multiple Student's t-tests were performed. *P≤0.05 compared with the peak; **P≤0.01 compared with the peak. Black and blue asterisks represent the P-values for acute and late infection, respectively. T: T cells; B: B cells; NK: natural killer cells; Grans: Ganulocytes; Eos: Eosinophils; Monos: monocytes; sBMDCe: sorted dendritic cell-enriched BMCs; Mac: Macrophages; HSCs: haematopoietic stem cells; HSPCs: haematopoietic stem cell and progenitor cells; MPP: multipotent progenitor cells; CLP: common lymphoid progenitor cells; CMP: common myeloid progenitor cells; MDP: macrophage-DC progenitors; MEP: megakaryocyte-erythrocyte progenitor;