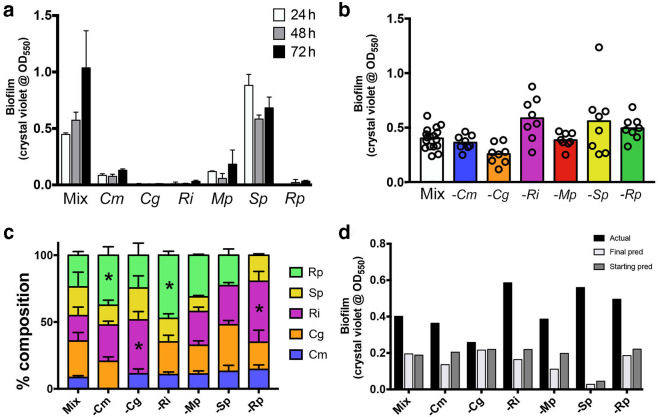
Fig. 1.
Biofilm formation related to species composition in the model drinking water community. (a) Biofilm formation increases over time for the full community; only S. paucimobilis forms substantial biofilms alone. (b) Biofilm formation for the full community and each community lacking one member. While there are trends, none of the groups are significantly different from the full community. (c) Species composition of the five species measured by c.f.u. counts. There is a strong interaction between changes in species compositions and the different community compositions by two-way ANOVA (P<0.0001), even when controlling for the missing members. Statistically significant changes in a species’ % composition compared to the full community was assessed using Dunnett’s post-test after the two-way ANOVA, with changes significant at P<0.01 being noted with an asterisk (*). (d) Comparison of actual biofilm means [from panel (b)] to the predicted biofilm formation using the compositions at the start or end of the experiment with the biofilm formation by each species on its own [panel (a)]. All data are from at least three independent biological experiments, each with at least two technical replicates per experiment. Mix, complete community; Cm, Cupriavidus metallidurans ; Cg, Chryseobacterium gleum ; Ri, Ralstonia insidiosa ; Mp, Methylorubrum populi ; Sp, Sphingomonas paucimobilis ; Rp, Ralstonia pickettii ; pred, prediction. ‘−’ denotes that that community member has been left out.