Fig. 1.
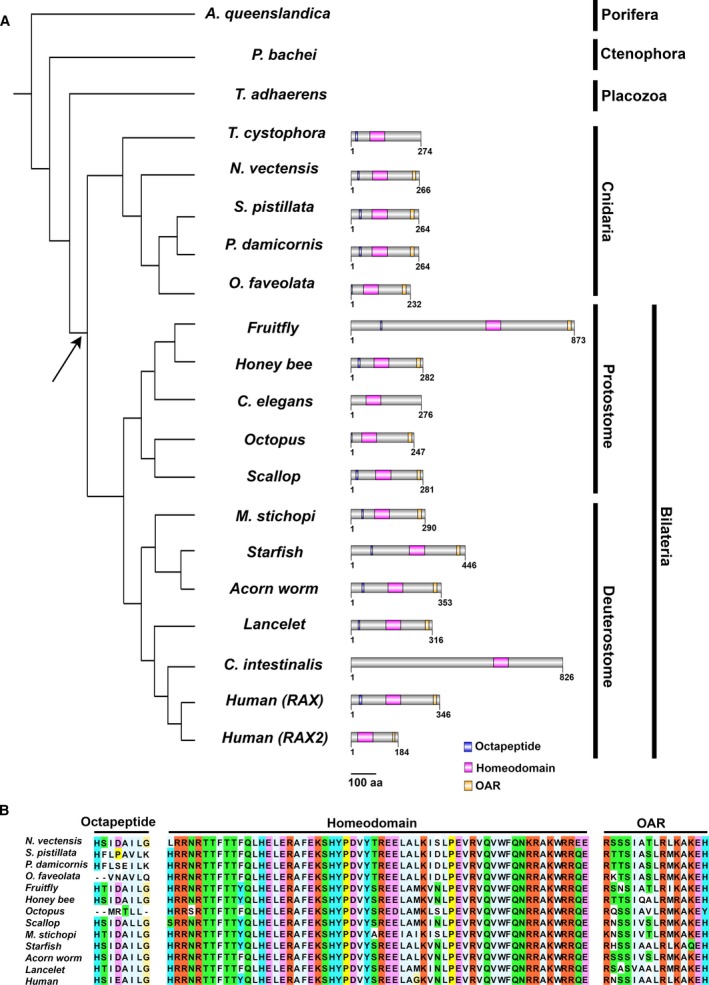
Phylogeny of animal species and their Rax genes. (A) Cladogram of representative animals and domain organizations of their Rax genes. Note the absence of Rax in Ctenophora, Porifera, and Placozoa. Blue boxes indicate octapeptides, magenta boxes indicate homeodomains, and yellow boxes indicate OAR motifs. The cladogram topology is derived from previous studies [54, 55, 56, 57]. It should be noted that the Metazoan phylogeny is controversial. The arrow indicates the presumed origin of the Rax gene. The scale bar indicates 100 amino acid residues. (B) Sequence alignments of the octapeptide, homeodomain, and OAR motif in Rax orthologs. These three domains/motifs are well conserved in Cnidaria and Bilateria. Each residue is colored according to the Clustal X residue code [58].
