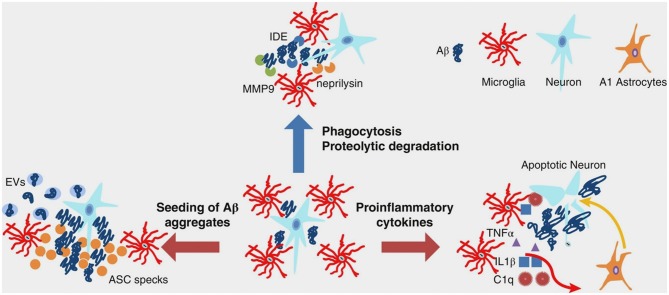
Figure 1.
Multifaceted functions of microglia during Aβ pathology. In healthy brain and early stages of AD, microglia clear small aggregates of Aβ peptides by phagocytosis and by secreting proteolytic enzymes, such as IDE, neprilysin, and MMP9. During advanced AD, microglia exacerbate AD pathology by releasing proinflammatory cytokines that induce neuronal cell death as well as A1 astrocytes, which, in turn, affect neuronal survival. Moreover, during advanced AD, microglia-derived ASC specks and EVs promote seeding of Aβ aggregates. Aβ, amyloid beta; AD, Alzheimer's disease; ASC, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD; C1q, complement component 1q; EVs, extracellular vesicles; IDE, insulin degrading enzyme; IL-1β, interleukin-1 beta; MMP-9, metalloprotease-9; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha. From Wang and Colonna (45). Copyright© 2019, Society for Leukocyte Biology. Reprinted with permission from Wiley.