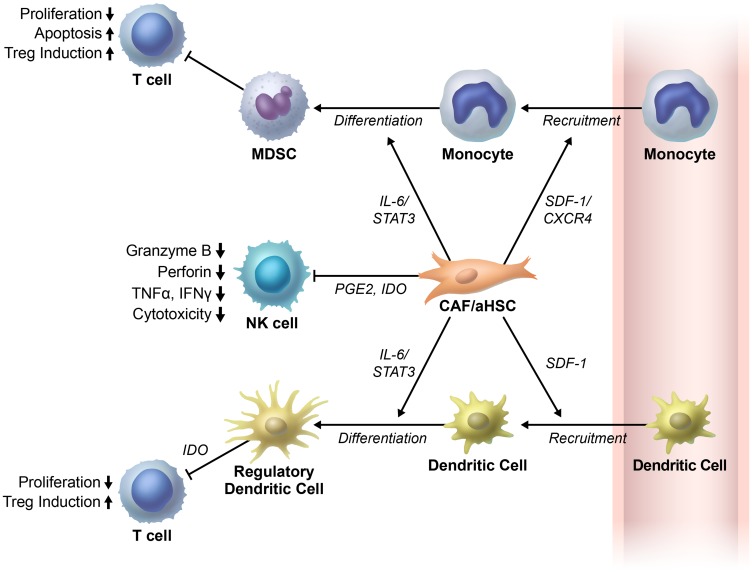
Figure 3. Cancer associated fibroblasts/activated hepatic stellate cells regulate immune cells in tumor microenvironment.
Cancer associated fibroblasts/activated hepatic stellate cells (CAFs/aHSCs) inhibit T-cell proliferation directly (not shown in figure) or indirectly. They first recruit the monocytes and dendritic cells. Thereafter, CAFs/aHSCs differentiate the monocytes and dendritic cells to myeloid derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and regulatory dendritic cells, respectively. Subsequently, these cells exhibit immunosuppressive functions in the tumor microenvironments. Moreover, the cancer associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in the liver impair NK cell functions. The NK cells play important roles in the anti-tumor immune response through prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO). Abbreviations: SDF, stromal cell-derived factor.