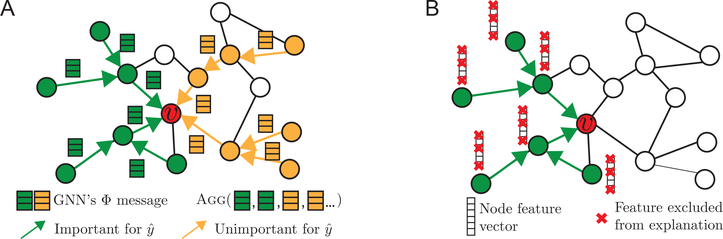
Figure 2:
A. GNN computation graph Gc (green and orange) for making prediction at node v. Some edges in Gc form important neural message-passing pathways (green), which allow useful node information to be propagated across Gc and aggregated at v for prediction, while other edges do not (orange). However, GNN needs to aggregate important as well as unimportant messages to form a prediction at node v, which can dilute the signal accumulated from v’s neighborhood. The goal of GnnExplainer is to identify a small set of important features and pathways (green) that are crucial for prediction. B. In addition to GS (green), GnnExplainer identifies what feature dimensions of GS’s nodes are important for prediction by learning a node feature mask.