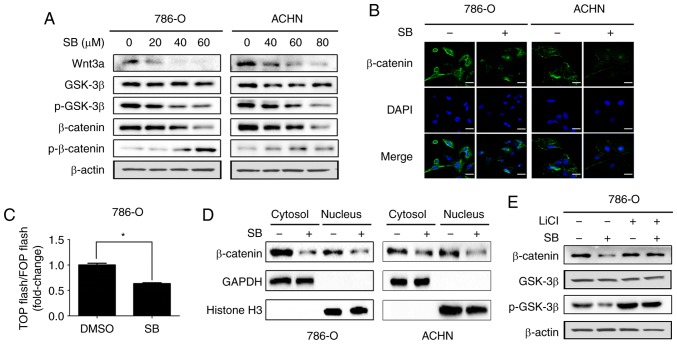
Figure 3.
SB inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling in RCC cells. (A) Western blot analysis of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway associated protein expression levels in 786-O and ACHN cells treated with different doses of SB for 24 h. β-actin was used as the loading control. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of β-catenin in 786-O and ACHN cells treated with 60 μM of SB for 24 h. Scale bars, 20 μm. (C) 786-O cells were transfected with TOP-flash or FOP-flash and treated with 60 μM SB for 24 h before measuring luciferase activity by measuring the ratio between TOP and FOP. Relative luciferase activity is represented as the mean ± standard deviation from each sample after normalizing to the control, *P<0.05. (D) 786-O cells were treated with 60 μM SB for 24 h. Western blotting was used to detect the cytosolic and nuclear expression levels of β-catenin. GAPDH and histone H3 were used as the cytosolic and nuclear controls, respectively. (E) 786-O cells were pre-treated with 20 mM LiCl for 6 h and subsequently treated with 60 μM SB treatment for 24 h and western blot analysis was used to detect the protein expression levels of p-GSK3β, total GSK3β and β-catenin. TOP-flash, TCF-responsive promoter reporter; FOP-flash, nonresponsive control reporter; SB, silibinin; p-GSK, phosphorylated-glycogen synthase kinase.